Photosynthesis Descriptive Ans Concise Biology Selina Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Ch-6. In this article you will get the solutions of Descriptive Type Questions as council latest syllabus. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.

Photosynthesis Descriptive Ans Concise Biology Selina Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Ch-6
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10 |
| Book | Selina Concise |
| Chapter-6 | Photosynthesis |
| Topics | Solutions of Descriptive Type Questions |
| Session | 2024-25 |
Solutions of Descriptive Type Questions on Photosynthesis
Que-1: Define the following terms:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Thylakoids
(c) Chloroplast
(d) Photolysis of water
(e) Polymerisation
Sol:
(a) Photosynthesis — Photosynthesis is the process by which living plant cells, containing chlorophyll, produce food substances (glucose and starch), from carbon dioxide and water, by using light energy and release oxygen as a by-product.
(b) Thylakoids — Closely packed flattened sacs arranged in piles in the interior of chloroplasts are called Thylakoids.
(c) Chloroplast — Chloroplasts are minute oval bodies bounded by a double membrane which contains Thylakoids arranged in piles called Grana lying in a colourless ground substance called Stroma.
(d) Photolysis of water — Photolysis of water is defined as the splitting of H2O molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen in the presence of light.
(e) Polymerisation — Polymerisation is the process in which several glucose molecules are transformed to produce one molecule of starch.
Que-2: Given below is the figure of an experimental set-up, showing a physiological act of the plants. Study and answer the following questions.
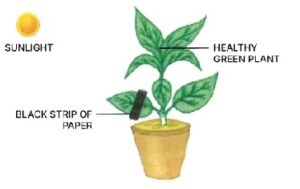
(a) What is the objective of this experiment ?
(b) Name and define the process shown here.
(c) Why do we destarch the leaves before performing the experiment ?
(d) How do we destarch the leaves ?
(e) What will be the observation when we pour iodine solution over the bleached experimental leaf.
(f) Write a well-balanced equation of the above process.
Sol:
(a) The objective of given experiment is to show that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
(b) The process shown here is photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which living plant cells, containing chlorophyll, produce food substances (glucose and starch), from carbon dioxide and water, by using light energy and release oxygen as a by-product.
(c) We destarch the leaves before experiment in order to remove the starch from leaves so that occurence of photosynthesis can be detected.
(d) To destarch the leaves the plant is kept in dark for 24-48 hours. This stops photosynthesis in the plant. During this time the starch already present in the leaves is translocated to storage organ of the plant fom the leaves.
(e) When we pour iodine solution over the bleached experimental leaf the area where starch is present turns blue.
(f) The equation for photosynthesis is given : 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Que-3: Give Reason / Explain:
(a) It is necessary to place a plant in the dark before starting an experiment on photosynthesis.
(b) It is not possible to demonstrate respiration in a green plant kept in sunlight.
(c) Most leaves have the upper surface more green and shiny than the lower surface.
(d) During the starch test, the leaf is -1. boiled in water. 2. boiled in methylated spirit.
Sol:
(a) A plant used for experiments on photosynthesis should initially be placed in the dark for 24 to 48 hours to destarch the leaves. During this period, all the starch will be removed from the leaves and stored in the storage organs. The leaves will not show the presence of starch. So the various experiments on photosynthesis can be carried out effectively.
(b) If a green plant is kept in bright light, it tends to use up all the CO2 produced during respiration, for photosynthesis. Thus, the release of CO2 cannot be demonstrated. Hence, it is difficult to demonstrate respiration as these two processes occur simultaneously.
(c) Due to more amount of chlorophyll on the upper surface more light is trapped. The chloroplasts are concentrated in the upper layers of the leaf which helps cells to trap the sunlight quickly. The upper surface is more green and shiny because it has a waxy coating to prevent loss of water due to evaporation.
(d) During the starch test, 1. The leaf is boiled in water to kill the cells. 2. The leaf is boiled in methylated spirit till it becomes pale-white due to the removal of chlorophyll. The leaf now becomes hard and brittle.
Que-4: Distinguish between the following pairs on the basis of words indicated in the brackets ( )
(a) Light reaction and Dark reaction (end products)
(b) Producers and Consumers (organisms)
(c) Grass and Grasshopper (mode of nutrition)
(d) Stoma and Stroma (structure)
Sol:
(a) Differences between light reaction and dark reaction (end products)
| Light Reaction | Dark Reaction |
|---|---|
| ATP and NADPH are the end products of this reaction. | Glucose is the main product formed during dark reaction. |
| The water molecule split into hydrogen and oxygen. | No splitting of water. |
( b) Differences between producers and consumers (organisms) –
| Producers | Consumers |
|---|---|
| They are autotrophs. | These are heterotrophs. |
| These can convert inorganic substances into organic substances. | They cannot convert inorganic substances into organic substances. |
| It includes green plants and photosynthetic micro-organisms. | It includes herbivores and carnivores. |
| For example — green plants | For example — Animals |
(c) Differences between grass and grasshopper (mode of nutrition) —
| Grass | Grasshopper |
|---|---|
| Green grass being a producer is capable of producing its own food by photosynthesis. | Grasshopper is a primary consumer (herbivore) and directly feeds on producers like grass. |
(d) Differences between stoma and stroma (structure)
| Stoma | Stroma |
|---|---|
| A stoma is a microscopic pore surrounded by two specialized guard cells found in the leaves and stems. Its main function is gaseous exchange. | Stroma is the colourless ground substance found in the chloroplast. It is the site of the light independent reactions of photosynthesis |
Que-5: How would you demonstrate that green plants release oxygen when exposed to light?
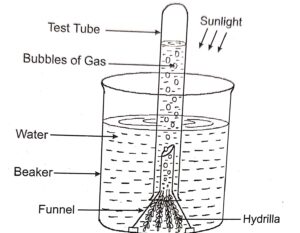
Sol:
- Place some water plants (Elodea or Hydrilla) in a beaker containing pond water and cover them by a short-stemmed funnel.
- Invert a test-tube full of water over the stem of the funnel. (Ensure that the level of water in the beaker is above the level of stem of the inverted funnel).
- Place the apparatus in the sun for a few hours. Bubbles of the gas will collect in the test-tube.
- Test the gas in the test-tube. A glowing splinter bursts into flame which shows the presence of oxygen.
Que-6: Describe the main chemical changes which occur during photosynthesis in 1. Light Reaction 2. Dark Reaction
Sol:
Light reaction
Light reaction occurs in two main steps
Step-1: Activation of chlorophyll:- The chlorophyll on exposure to light energy becomes activated by absorbing photons.
Step-2: Splitting of Water: The absorbed energy is used in splitting the water molecule (H2O) into its two components (Hydrogen and Oxygen) and releasing electrons This reaction is known as photolysis of water
End result of the products of photolysis: The hydrogen ions (H+) are picked up by a compound NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) to form NADPH
The electrons (e–) are used in converting ADP (adenosine diphosphate) into energy rich compound ATP (adenosine triphosphate) by adding one phosphate group Pi (inorganic phosphate)
Dark Reaction
The reactions in this phase do not require light energy and occur simultaneously with the light reaction. The time gap between the light and dark reaction is less than one thousandth of a second. In the dark reaction, ATP and NADPH molecules (produced during light reaction) are used to produce glucose (C6H12O6) from carbon dioxide. Fixation and reduction of carbon dioxide occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast through a series of reactions. The glucose produced is either immediately used up by the cells or stored in the form of starch
–: End of Photosynthesis Descriptive Ans Concise Biology Selina Solutions :–
Please share with your friend if helpful
Return to : Concise Biology for ICSE Class 10 Selina Solutions
Thanks


