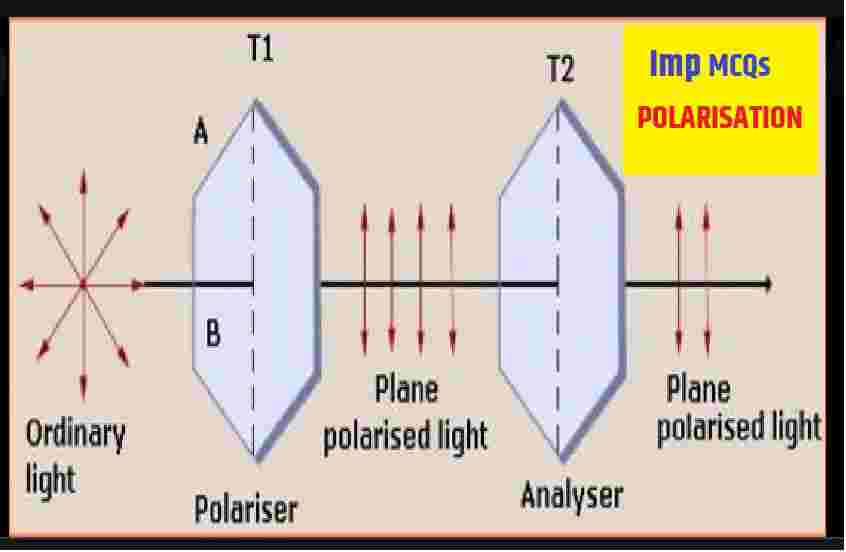
Polarisation of Light: MCQs Type Imp Que with Ans for ISC Class 12 Physics . These MCQs / Objective Type Questions is based on latest reduced syllabus according 2021-22 session on bifurcated pattern. Main motto of MCQ Type Question is cracking the next upcoming Sem-2 exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ISC Class-12 Physics.
Polarisation of Light: MCQs Type Imp Que with Ans for ISC Class 12 Physics
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12th (XII) |
| Subject | Physics |
| Chapter | Polarisation of Light |
| Syllabus | on bifurcated syllabus (after reduction) |
| Session | 2021-22 |
| Bifurcated | Sem-2 |
| Topic | MCQs / Objective Type Question |
MCQs Type Imp Que with Ans of “Polarisation of Light” ISC Class 12 Physics
Question 1. Which type of waves shows the property of polarization?
(a) Infrared
(b) Longitudinal
(c) Transverse
(d) Microwave
Answer: (c) Transverse
Question 2. What will be the angle of refraction in the glass, if the polarization angle for the air-glass interface is 63.8o?
(a) 56.3o
(b) 33.7o
(c) 90o
(d) 0o
Answer: (b) 33.7o
Question 3. What is the polarization angle of a medium of refractive index √3?
(a) 60o
(b) 120o
(c) 30o
(d) 90o
Answer: (a) 60o
Question 4. What are sunglasses made of?
(a) Colored glasses
(b) Tin glass
(c) Silica
(d) Polaroids
Answer: (b) Tin glass
Question 5. Which field vector is used to represent the polarization of an em wave?
(a) Potential field vector
(b) Magnetic field vector
(c) Electric field vector
(d) Dipolar field vector
Answer: (c) Electric field vector
Question 6. Sound waves can be polarized.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (b) False
Question 7. Identify the property which is not mutually perpendicular to the polarized light wave in a plane.
(a) Plane of vibration
(b) Plane of rotation
(c) Plane of polarization
(d) The direction of propagation of the light wave
Answer: (b) Plane of rotation
Question 8. Which plane is defined as the plane of polarization in a plane-polarized electromagnetic wave?
(a) The plane containing the direction of propagation of light
(b) The plane containing the direction of reflective wave
(c) The plane containing the direction of refractive wave
(d) The plane containing the direction of dispersive wave
Answer: (a) The plane containing the direction of propagation of light
Question 9. In the propagation of light waves, the angle between the plane of vibration and plane of polarisaiton is
(a) 90º
(b) 45º
(c) 80º
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) 90º
Question 10. The phenomenon of diffraction can be treated as interference phenomenon if the number of coherent sources is
(a) infinity
(b) zero
(c) two
(d) one
Answer: (a) infinity
Question 11. From Brewster’s law of polarisation, it follows that the anlge of polarisaiton depends upon
(a) the wavelength of light
(b) plane of polarisation’s orientation
(c) plane of vibration’s orientation
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) the wavelength of light
Question 12. A 20 cm long tube containing 15% sugar solution rotates the plane of polarization of light by 21°. The specific rotation of sugar solution is:
(a) 64°
(b) 70°
(c) 58°
(d) 49°
Answer: (b) 70°
Question 13. The critical angle of glass w.r.t air is 35.26o. What is the angle of refraction for light, incident on glass at polarization angle? (sin 35.26o = 0.577)
(a) 30o
(b) 45o
(c) 60o
(d) None
Answer: (a) 30o
Question 14. When a beam of ordinary light is passed through a calcite crystal, the light splits into O-ray and E-ray inside the crystal.
(a) Only O-ray is polarised
(b) Neither E-ray nor O-ray is polarised
(c) Only E-ray is polarised
(d) Both E-ray and O-ray are polarised
Answer: (d) Both E-ray and O-ray are polarised
Question 15. Calculate phase difference introduced by a calcite crystal plane of thickness 30 microns between ordinary and extraordinary light of wavelength 6000 Å. Given that μ0 = 1.554 and μe = 1.547
(a) 0.4π
(b) 0.7 π
(c) 0.9 π
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) 0.7 π
Question 16. The light has ____ nature.
(a) wave
(b) particle
(c) matter
(d) dual nature
Answer: (d) dual nature
Question 17. Polarised light can be produced by:
(a) NaCl crystal
(b) Nicol prism
(c) Biprism
(d) Prism made of flint glass
Answer: (b) Nicol prism
Question 18. Which of the following phenomena establishes the transverse nature of light waves?
(a) Polarisation
(b) Diffraction
(c) Photoelectric effect
(d) Compton effect
Answer: (a) Polarisation
Question 19. When light from a single point passes through calcite, it often forms two images. Each of two images are formed from light that has been polarised by:
(a) Scattering
(b) Double refraction
(c) Reflection
(d) Selective absorption
Answer: (b) Double refraction
Question 20. The specific rotation of a 10% sugar solution is 60°. If the length of the polarimeter tube containing sugar solution is 20 cm, the plane of polarisation of light is rotated by:
(a) 24°
(b) 12°
(c) 19°
(d) 31°
Answer: (b) 12°
Question 21. An unpolarised beam is incident at an angle 60° an a glass surface and after reflection it is linearly polarised. The approximate refractive index of the glass is:
(a) 1.4
(b) 1.5
(c) 1.7
(d) 1.6
Answer: (c) 1.7
Question 22. If light is allowed to pass through two polaroids ‘P1‘ and ‘P2‘ and ‘Io‘ is the intensity of the polarized light after passing through ‘P1‘, then the intensity of light (I) coming out from ‘P2‘ will vary as ____________.
(a) I = Iocos2 θ
(b) I = Iocos θ
(c) I = Io2cos2 θ
(d) I = Io2cos θ
Answer: (a) I = Iocos2 θ
Question 23. Nature of electromagnetic waves is transverse. Evidence of this is given by
(a) Interference
(b) Polarisation
(c) Diffraction
(d) Reflection
Answer: (b) Polarisation
Question 24. What happens when the sunlight pass through a uniaxial crystal?
(a) Interference
(b) Polarization
(c) Scattering
(d) Diffraction
Answer: (b) Polarisation
Question 25. The phenomenon of polarization shows that light has _____ nature.
(a) particle
(b) transverse
(c) longitudinal
(d) dual
Answer: (b) transverse
Question 26. The waves forming ordinary image are
(a) plane polarised
(b) unpolarised
(c) partially polarised
(d) any of above
Answer: (a) plane polarised
Question 27. The Specific rotation is
(a) independent of wavelength
(b) directly proportional to wavelength
(c) inversely proportional to wavelength
(d) inversely proportional to square wavelength
Answer: (d) inversely proportional to square wavelength
Question 28. The angle substanded by the first diffraction minimum for a point source viewed in the hydrogen line at 1420 MHz with a radio telescope having an aperture of 25 m is
(a) 1.2°
(b) 2.2°
(c) 0.64°
(d) 0.8°
Answer: (a) 1.2°
Question 29. From Brewster’s law of polarisation, it follows that the anlge of polarisaiton depends upon
(a) the wavelength of light
(b) plane of polarisation’s orientation
(c) plane of vibration’s orientation
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) the wavelength of light
Question 30. A linearly polarized wabe is always __________
(a) In x-y plane
(b) A Transverse wave
(c) A Longitudinal wave
(d) In y-z plane
Answer: (b) A Transverse wave
Question 31. The direction in which the electric vectors oscillate in a polarized wave is called as _______
(a) Polarizing axis
(b) Plane of polarization
(c) Pass axis
(d) Propagating axis
Answer: (c) Pass axis
Question 32. If the phase difference between two rays is π/2 and the angle of incidence is equal to π/4, the emergent light is __________
(a) Linearly Polarized
(b) Elliptically Polarized
(c) Circularly Polarized
(d) Non-Polarized
Answer: (c) Circularly Polarized
Question 33. The velocity of light in water is 1.5 X 108 m/s. What is the polarizing angle of incidence?
(a) 47.23°
(b) 51.02°
(c) 53.74°
(d) 63.43°
Answer: (d) 63.43°
Question 34. What should be the thickness of quarter-wave plate for a light of wavelength 5000 Å if µe = 1.553 and µo = 1.544?
(a) 1.38 X 10-3 cm
(b) 1.43 X 10-3cm
(c) 1.53 X 10-3cm
(d) 1.63 X 10-3 cm
Answer: (a) 1.38 X 10-3 cm
Question 35. A plate which induces the desired amount of phase difference between two rays is known as ____________
(a) Polaroid
(b) Phasor plates
(c) Retardation Plates
(d) Quartz plates
Answer: (c) Retardation Plates
–: End of Polarisation of Light: MCQs :–
-: also visit :-
- ISC Sem-2 Question Bank Class-12
- Sem-2 ISC Specimen Paper for Class-12
- ISC Class-12 Textbook Solutions ,Syllabus, Solved Paper
- Previous Year Question Paper for ISC Class-12
Please share with your ISC friends if it is helpful
Thanks