Rest and Motions Kinematics Obj-1 (MCQ-1) HC Verma Solutions Ch-3 Vol-1 Concept of Physics for Class-11. Step by Step Solution of Objective -1 (MCQ-1) Questions of Chapter-3 Rest and Motions Kinematics (Concept of Physics) .Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-11 Physics.
Rest and Motions Kinematics Obj-1 (MCQ-1) HC Verma Solutions Ch-3 Vol-1 Concept of Physics for Class-11
| Board | ISC and other board |
| Publications | Bharti Bhawan Publishers |
| Chapter-3 | Rest and Motions Kinematics |
| Class | 11 |
| Vol | 1st |
| writer | HC Verma |
| Book Name | Concept of Physics |
| Topics | Solution of Objective-1 (MCQ-1) Questions |
| Page-Number | 49 , 50 |
-: Select Topics :-
Question for Short Answer
Objective-I (Currently Open)
Objective-II
Exercise
Rest and Motions Kinematics Obj-1 (MCQ-1)
HC Verma Solutions of Ch-3 Vol-1 Concept of Physics for Class-11
(Page-49)
Question-1
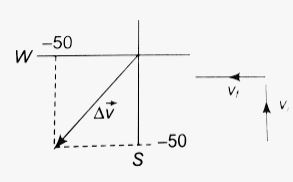
A motor car is going due north at a speed of 50 km/h. It makes a 90° left turn without changing the speed. The change in the velocity of the car is about
(a) 50 km/h towards west
(b) 70 km/h towards south-west
(c) 70 km/h towards north-west
(d) zero
Answer-1
The option (b) 70 km/h towards south-west. is correct
Explanation:
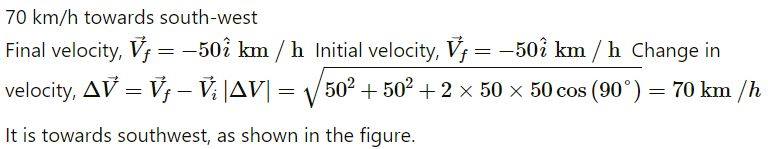
Question-2
In figure shows the displacement-time graph of a particle moving on the X-axis.
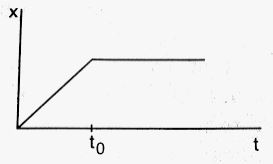
(a)the particle is continuously going in positive x direction
(b) the particle is at rest
(c) the velocity increases up to a time t0, and them become constant
(d) the particle moves at a constant velocity up to a time t0, and then stops.
Answer-2
The option (d) the particle moves at a constant velocity up to a time t0, and then stops. is correct
Explanation:
The particle moves at a constant velocity up to a time t0 and then stops.
The slope of the x–t graph gives the velocity. In the graph, the slope is constant from t = 0 to t = t0, so the velocity is constant. After t = t0, the displacement is zero; i.e., the particle stops.
Question-3
A particle has a velocity u towards east at t = 0. Its acceleration is towards west and is constant. Let xA and xB be the magnitude of displacements in the first 10 seconds and the next 10 seconds
(a) xA < xB
(b) xA = xB
(c) xA > xB
(d) the information is insufficient to decide the relation of xA with xB.
Answer-3
The option (d) the information is insufficient to decide the relation of xA with xB. is correct
Explanation:
As velocity and acceleration are in opposite directions, velocity will become zero after some time (t) and the particle will return.
∴0 = u− a t
⇒ t= u/a
Because the value of acceleration is not given, we cannot say that the particle will return after/before 10 seconds.
Question-4
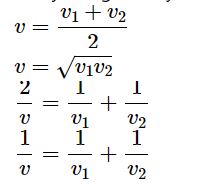
Answer-4
The option (a) v = (v1+ v2) / 2 is correct
Explanation:
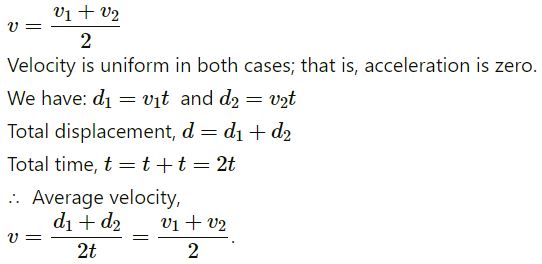
Question-5
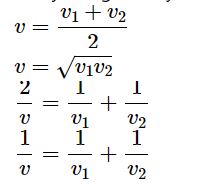
Answer-5
The option (c) is correct
Explanation:
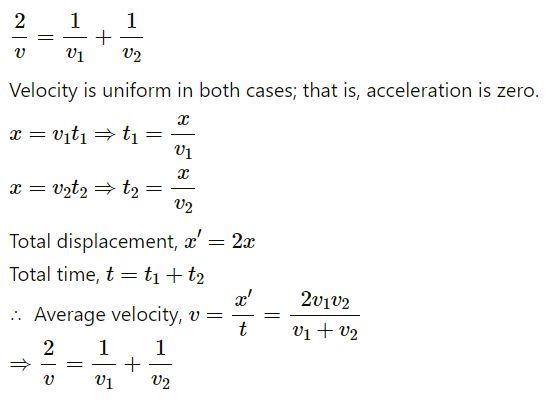
Question-6
(a) a upward
(b) (g − a) upward
(c) (g − a) downward
(d) g downward
Answer-6
The option (d) g downward is correct
Explanation:
Gravity is the only force acting on the stone when it is released. And, we know that gravity is always in the downward direction
Question-7
(a) vA > vB
(b) vA < vB
(c) vA = vB
(d) the relation between vA and vB depends on height of the building above the ground.
Answer-7
The option (c) vA = vB is correct
Explanation:
Total energy of any particle =
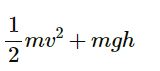
Both the particles were at the same height and thrown with equal initial velocities, so their initial total energies are equal. By the law of conservation of energy, their final energies are equal.
At the ground, they are at the same height. So, their P.E. are also equal; this implies that their K.E. should also be equal. In other words, their final velocities are equal
Question-8
(a) is always perpendicular to the acceleration
(b) is never perpendicular to the acceleration
(c) is perpendicular to the acceleration for one instant only
(d) is perpendicular to the acceleration for two instants.
Answer-8
The option (c) is perpendicular to the acceleration for one instant only is correct
Explanation:
Question-9
Two bullets are fired simultaneously, horizontally and with different speeds from the same place. Which bullet will hit he ground first?
(a) the faster one
(b) the slower one
(c) both will reach simultaneously
(d) depends on the masses.
Answer-9
The option (c) both will reach simultaneously is correct
Explanation:
Because the downward acceleration and the initial velocity in downward direction of the two bullets are the same, they will take the same time to hit the ground and for a half projectile.
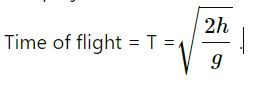
Question-10
(a) 25 m
(b) 37 m
(c) 50 m
(d) 100 m
Answer-10
The option (d) 100 m is correct
Explanation:
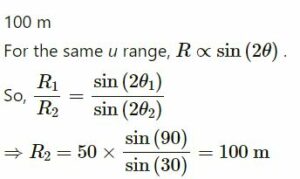
Question-11
Two projectiles A and B are projected with angle of projection 15° for the projectile A and 45° for the projectile B. If RA and RB be the horizontal range for the two projectiles, then
(a) RA < RB
(b) RA > RB
(c) RA = RB
(d) the information is insufficient to decide the relation of RA with RB.
Answer-11
The option (d) the information is insufficient to decide the relation of RA with RB. is correct
Explanation:
Horizontal range for the projectile,
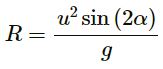
Information of the initial velocity is not given in the question
Question-12
A river is flowing from west to east at a speed of 5 metres per minute. A man on the south bank of the river, capable of swimming at 10 metres per minute in still water, wants to swim across the river in the shortest time. He should swim in a direction.
(a) due north
(b) 30° east of north
(c) 30° north of west
(d) 60° east of north.
Answer-12
The option (a) due north is correct
Explanation:
If the man swims at any angle east to the north direction, although his relative speed will increase, he will have to travel a larger distance. So, he will take more time.
Question-13
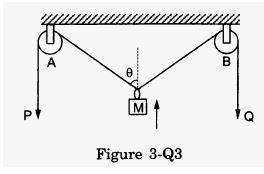
(a) 2u cos θ
(b) u/cos θ
(c) 2u/cos θ
(d) u cos θ
Answer-13
The option (b) u/cos θ is correct
Explanation:
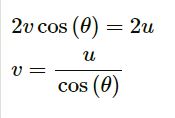
—: End of Rest and Motions Kinematics Obj-1 (MCQ-1) HC Verma Solutions Ch-3 Vol-I :–
Thanks