Srijan Class-9 Respiration in plants ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-6. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check-1, and 2,Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type ( including True False), Application / Skill ( Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Solutions of Srijan Class-9 Respiration in plants ICSE Biology Ch-6.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-6 | Respiration in plants |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check-1, and 2, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Ch-6 Respiration in plants Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 1 (Page 65)
Fill in the blanks with suitable words :
1. The process of energy release during respiration is a cellular process.
2. Enzyme take part in respiration while no enzyme is involved in burning.
3. ATP is called the energy currency of the cell.
4. In young root, the exchange of gases occurs between cell membrane and soil particles.
5. Exchange of gases takes place through lenticels in old roots and wood stems.
Concept Check 2 (Page 70)
Srijan Publishers ICSE Biology Solutions of Ch-6 Respiration in plants
State whether the following statements are true or false, If false, write the correct statement by changing the incorrect word/words only.
1. Respiration is biochemical process controlled by enzymes. True
2. Fermentation is an example of anaerobic respiration. True
3. Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration and is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. True
4. Aerobic respiration of one mole of glucose yields 38 ATP. True
5. Latic acid is produced during anaerobic respiration by plants. False
6. The leaves of a green plants normally respire anaerobically during night. False
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 70)
Ch-6 Respiration in plants ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
Question 1:
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) Respiration is a process perform to photosynthesis.
(b) In photosynthesis, sun’s energy is converted to chemical energy.
(c) CO2 lactic acid and ethyl alcohol are formed during anaerobic respiration.
(d) Rate of photosynthesis is more than the rate of respiration during daytime in case of green plants.
(e) Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells.
(f) Aerobic respiration requires oxygen
(g) Each step of respiration is controlled by a enzymes.
Question 2:
Give proper term for each of the following :
(a) Biological oxidation of glucose into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen.
(b) Conversion of glucose molecule into pyruvic acid in a sequence of chemical reactions.
(c) The organelles where Krebs cycle takes place.
(d) Conversion of pyruvic acid into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide in the absence of oxygen.
(e) Conversion of pyruvic acid into CO2 and water in the presence of oxygen.
(f) The breathing roots in plants growing in swamps.
(g) The place where the process of glycolysis occurs in a cell.
(h) The phase of respiration which is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer :
(a) Respiration
(b) Glycolysis
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Anaerobic respiration
(e) Krebs Cycle
(f) Mangrove
(g) Cytoplasm
(h) Glycolysis
Question 3:
Write the following:
(a) The balanced equation of aerobic respiration.
(b) The number of molecules of ATP formed during complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose.
Answer :
(a) C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 ——-> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
(b) 38 ATP
Respiration in plants ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
B. Short Answer Type Questions (Page 71)
Question 1:
Give reasons for the following:
(a) More energy is released in aerobic respiration than in anaerobic respiration.
(b) Although both food and oxygen are necessary for life, man can live without food for a number of days, but he dies without oxygen within a few minutes.
Answer :
(a) Much less energy is released during anaerobic respiration than during aerobic respiration. This is because the breakdown of glucose is incomplete. Anaerobic respiration produces an oxygen debt. This is the amount of oxygen needed to oxidise lactic acid to carbon dioxide and water
(b) Because Oxygen Is necessary for Breathing and our Blood Needs fresh oxygen to supply it to all parts of our body. When our body needs energy this extra glycogen is converted in glucose again and therefore we can survive for some days without Food
Question 2:
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Respiration and combustion
(b) Photosynthesis and respiration
(c) Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
(d) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
Answer :
(a) Difference Between Respiration and Combustion
|
Respiration |
Combustion |
|
Glucose is broken down in living cells with the process called respiration. |
Combustion of substances such as wood and kerosene releases lots of energy. |
|
Inside the cells, many chemicals participate in the long chains of reactions to breakdown glucose into simpler substances and the energy released in different steps is saved in the form of ATP. |
It is not a process taking place inside our cells. |
|
It takes place in a controlled manner inside the cells. |
It is an uncontrollable process. |
|
Heat is produced in the cellular respiration. Example, the rate of respiration increases when we exercise and we feel warmer. |
It produces energy as waste and heat. |
|
It is much more efficient. |
It is less efficient as compared to the respiration process. |
|
Different chemicals break glucose step by step. |
Heat breaks down glucose |
|
It produces a large amount of energy stored as chemical energy. |
It produces energy waste as heat. |
|
If temperature is allowed to rise, the cell may damage. |
The temperature during combustion can be very high and usually higher than respiration. |
|
One of the examples is aerobic respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen; and in life processes, glucose and oxygen is converted to carbon dioxide, water and energy from respiration. |
Its examples: Combustion of oxygen and hydrogen leading to the formation of water vapour; when we ignite the gas stove for cooking food; motor vehicle burning petrol and diesel for motion; burning wood for fire and producing heat. |
|
Respiration uses glucose to give pyruvate and then carbon dioxide. |
Any substance which can burn leads to a combustion process. |
|
ATP is the byproduct of respiration as energy is trapped in the form of ATP in respiration. |
It produces heat energy which is instantly utilised. |
|
There is no smoke formation. |
It produces oxides as smoke formation takes place. |
(b)
In the process of respiration, oxygen and glucose yield water and carbon dioxide, while carbon dioxide and water yield glucose and oxygen during the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis cannot occur without cellular respiration and cellular respiration certainly cannot occur without photosynthesis.
(c) Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Base | Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| Definition | Aerobic respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen, occurring in a cell to convert chemical energy into ATPs. | Anaerobic respiration is a process of cellular respiration where the high energy electron acceptor is neither oxygen nor pyruvate derivatives. |
| Overall equation | The overall equation of aerobic respiration is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy |
The overall equation of anaerobic respiration is:
C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + CO2 + energy |
| Presence of Oxygen | Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen. | Anaerobic respiration takes place in a condition where there is a low oxygen environment. |
| Exchange of gases | There is an exchange of gases during aerobic respiration where oxygen is absorbed, and carbon dioxide is released. | The exchange of gases doesn’t take place during anaerobic respiration. However, some gases like sulfur and nitrogen gases are released by some organisms. |
| Location | Aerobic respiration, after glycolysis, occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotes and cytoplasm of prokaryotes. | Anaerobic respiration occurs only in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| End products | The end products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and energy. | The end products of anaerobic respiration are acids, alcohols, gases, and energy. |
| Energy produced | A total of 38 ATPs are produced during aerobic respiration, some of which are lost during the process. | Only 2 ATPs are formed during anaerobic respiration. |
| Reactants | Carbohydrates and oxygen are the prerequisites of aerobic respiration. | Some other electron acceptors like sulfur and nitrogen are required along with the carbohydrates. |
| Oxidation | Complete oxidation of carbohydrates takes place during aerobic respiration. | Incomplete oxidation of carbohydrates takes place during anaerobic respiration. |
| Nature of the process | Aerobic respiration is comparatively longer than anaerobic respiration. | Anaerobic respiration is shorter than aerobic respiration. |
| Occurs in | Aerobic respiration occurs in most of the higher organisms like plants and animals. | Anaerobic respiration occurs in primitive prokaryotes. Anaerobic respiration also takes place in the muscle cells in humans during extreme movements. |
(d) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
Glycolysis – It is an anaerobic process, which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. In glycolysis, partial oxidation of glucose occurs, which yields two molecules of pyruvic acid.
Krebs Cycle – It is an aerobic process that takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. It gives Carbon dioxide after complete oxidation of pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis.
C. Long Answer Type Questions (Page 71)
Ch-6 Respiration in plants ICSE Class-9th Biology Solutions Srijan Publishers
Question 1:
(a) What is the net result of glycolysis and Krebs cycle?
(b) What is the advantage of stepwise release of energy in respiration?
Answer :
(a) Glycolysis is the major catabolic pathway for sugars. The process results in ATP and the intermediates that feed into the Krebs cycle and produce more ATP. The main products are 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, a net of two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate).
(b) In Stepwise — energy is released in stepwise manner to prevent damage of cells. A stepwise release of the chemical bond energy facilitates the utilization of a relatively higher proportion of that energy in ATP synthesis. Activities of enzymes for the different steps may be enhanced or inhibited by specific compounds
Question 2:
(a) How does a flowering plant exchange gases with the atmosphere?
(b) What are the various steps that affect the process of respiration?
Answer :
(a) the exchange of gases takes place through stomata. Each of the stomata is surrounded by two guard cells, and these cells contain chloroplasts. A respiratory opening is found under each stoma, and the process of opening and closing of stomata depends on the presence of sugar and starch in the guard cells.
(b) Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Question 3:
How will you prove that heat is produced during respiration?
Answer :
PROCEDURE :- Take some germinating seeds in a Thermos flask. Cover the flask with a cork. Insert the thermometer in the flask through the cork. Observe the rise in temperature after some time.
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE, (Page 71)
Ch-6 Respiration in plants Srijan Biology Solutions for ICSE Class-9
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1 :
Respiration is a
(a) Chemical process
(b) Mechanical process
(c) Vital process
(d) Physical process
Answer :
(a) Chemical process
Question 2 :
Anaerobic respiration occurs in
(a) Cacti
(b) Grass
(c) Trees
(d) Yeast
Answer :
(d) Yeast
Question 3 :
Number of CO2 molecules evolved in anaerobic respiration is:
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer :
(a) 2
E. Application/Skill-based Questions (Page 71)
Respiration in plants ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Question 1:
Describe an experiment to show that carbon dioxide is released during respiration in germinating seeds.
Answer :
Material Required
- Soaked gram seeds
- U-shaped delivery tube
- Conical flask
- Blotting paper (moist) /cotton wool
- Thread
- Water
- Beaker
- Test tube
- Rubber cork with a single hole
- Freshly prepared KOH solution (20%)
- Vaseline
Procedure
- Germinate close to 25 seeds. This can be done by wrapping them in moist blotting paper or cotton wool for around 3 to 4 days
- Set up the germinated or sprouted seeds in the conical flask. Spray some water into the flask to dampen the seeds
- With the help of a thread, suspend the conical flask containing the test tube having a freshly prepared 20% KOH solution.
- Use the rubber cork to seal the opening of the conical flask.
- One edge of the U-shaped glass delivery tube present in the conical flask should be inserted through the hole in the rubber cork. The other edge should be placed into a beaker that is saturated with water
- All attachments of the set-up should be sealed. This can be done using Vaseline to create an air-tight environment
- The initial water level present in the U-shaped delivery tube needs to be marked.
- Leave the experimental set-up uninterrupted for 1 to 2 hours. Observe the fluctuations in the water level in the tube.
Observation
Careful observation after a certain period of time reveals that the water level in the U-shaped delivery tube has risen in the beaker.
Conclusions
The rise in level water indicates that carbon dioxide is released as a result of germinating gram seeds during the process of respiration in the conical flask. The carbon dioxide that is released in the process is absorbed or consumed by the KOH solution that is suspended in the test tube in the conical flask, creating a vacuum or a void in the flask resulting in the upward water movement in the tube. Hence, the water level in the tube changes.
Question 2:
In order to study and prove a particular physiological process in plants, the following experiment was set up as shown in the figure. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
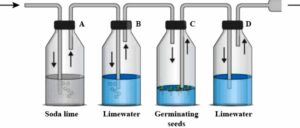
(a) Name the physiological process being studied.
(b) What is the function of soda lime in flask A and why is lime water placed in flask B?
(c) What changes would you expect to observe in flask D?
(d) Represent the physiological process in the form of a chemical equation in D.
(e) If flask C were fitted with a three-holed rubber stopper and a thermometer were introduced in such a way that its bulb reaches close to the germinating seeds, what would you observe and why?
Answer :
(a) The experiment demonstrates that carbon dioxide is produced during the process of respiration in
germinating seeds.
(b) Soda lime is placed in bottle ‘A’ as it indicates the passage/presence of carbon dioxide in bottle
A. Another property of soda lime is that it absorbs carbon dioxide that is present in the air. The clear limewater in bottle B indicates that the air that enters the flask C is free from carbon dioxide.
(c) The bottle D holding limewater should indicate that carbon dioxide is produced as a result of respiration occurring in bottle ‘C’ possessing the germinating seeds. As carbon dioxide is produced in the bottle C, limewater turns milky that enters the bottle ‘D’.
(d) The chemical reaction is as written below:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + 38 ATP (energy)
(e) The bottle ‘C’ is covered with a black cloth in order to restrict any chance of photosynthesis so as to make sure the process of respiration only is carried out and observed.
Question 3:
A student boiled some glucose solution and let it cool. She then added some yeast and set up the apparatus as shown in the figure. Answer the following questions :
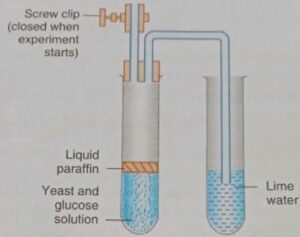
(a) Why was the glucose boiled and cooled?
(b)What is the purpose of the liquid paraffin?
(c)What process is being investigated?
(d) What result would you expect?
(e) After about an hour in a warm place, the tube containing the yeast felt warmer than the surroundings and there was a slight smell of alcohol. Explain these observations.
Answer :
To remove oxygen and create conducive temperatures for the yeast to work in
Explanation: The boiling is to remove oxygen, because the yeast needs to respire anaerobically to release alcohol. The glucose was cooled down to not kill the yeast. They work under very specific temperatures.
(b) after about an hour in warm place the tube
Thanks