Srijan Class-9 Skin-Structure and Functions ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-13. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check 1 to 2, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type Application / Skill ( Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Solutions of Srijan Publications Class-9 ICSE Biology Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-13 | Skin-Structure and Functions |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check 1 to 2, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Concept Check 1 (Page 147)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
Match the Column.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Arrector muscle | (a) Regulation of body temperature |
| 2. Hair | (b) Nitrogenous waste |
| 3. Receptor corpuscles | (c) Three layers |
| 4. Epidermis | (d) Sense of touch |
| 5. Sweat gland | (e) Goose flesh |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Arrector muscle | (e) Goose flesh |
| 2. Hair | (a) Regulation of body temperature |
| 3. Receptor corpuscles | (d) Sense of touch |
| 4. Epidermis | (c) Three layers |
| 5. Sweat gland | (b) Nitrogenous waste |
Concept Check 2 (Page 149)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
Match the Column.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Sweat | (a) Heat loss |
| 2. Vasodilation | (b) Winter |
| 3. Piloerection | (c) Summer |
| 4. Homeothermy | (d) Saltish |
| 5. Vasoconstriction | (e) Constant body temperature |
| 6. Sweating | (f) Heat conservation |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Sweat | (a) Heat loss |
| 2. Vasodilation | (c) Summer |
| 3. Piloerection | (f) Heat conservation |
| 4. Homeothermy | (e) Constant body temperature |
| 5. Vasoconstriction | (b) Winter |
| 6. Sweating | (d) Saltish |
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 150)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) The body temperature of a human-being remains almost constant at about 36.9°C.
(b) Hair are living structures.
(c) Widening of blood capillaries in the dermis increases heat loss from skin.
(d) Sebaceous glands are associated with temperature regulation of body.
(e) skin derivatives like hair, spines, scales are developed from the epidermis layer.
(f) Vasodilation occurs during summer to avoid loss of heat from blood.
(g) Sweat glands lubricate hair of eye lashes.
(h) The primary function of sweat glands is excretion.
Answer:
(a) True
(b) False
(c) True
(d) True
(e) True
(f) False
(g) False
(h) True
B. Short Answer Type Questions (Page 150)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
Q-1. Give one difference for each of the following
(a) Vasoconstriction and vasodilation
Ans-The main difference between vasodilation and vasoconstriction is that vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels whereas vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels
(b) Sweat and cerumen
Ans-
| Sweat | Sebum |
|---|---|
| Sweat is discharged from the surface of the skin. | Sebum is discharged from the hair follicles. |
(c) Stratum corneum and Stratum Malpighi
Ans- Stratum Malpighi is the innermost layer of the skin and is made up of columnar epithelium. The stratum corneum or the cornified layer is the outermost layer of cells consisting of several dead flat cells. … The middle granular layer is a thin layer made up of flat cells
(d) Mammary gland and Meibomian gland
Ans-
Meibomian gland: A type of gland in the eyelids that makes a lubricant called sebum which is discharged through tiny openings in the edges of the lids.
The meibomian glands can become inflamed, a condition termed meibomianitis or meibomitis, due to allergy, acne in adolescence, and rosacea.
Q-2. State the role of each of the following:
(a) Hair papilla
Ans- Hair dermal papilla cells are specialized mesenchymal cells that exist in the dermal papilla located at the bottom of hair follicles. These cells play pivotal roles in hair formation, growth, and cycling.
(b) Sebaceous glands
Ans- The normal function of sebaceous glands is to produce and secrete sebum, a group of complex oils including triglycerides and fatty acid breakdown products, wax esters, squalene, cholesterol esters and cholesterol. Sebum lubricates the skin to protect against friction and makes it more impervious to moisture.
(c) Sweat glands
Ans- Sweat glands are used to regulate temperature and remove waste by secreting water, sodium salts, and nitrogenous waste (such as urea) onto the skin surface. The main electrolytes of sweat are sodium and chloride, though the amount is small enough to make sweat hypotonic at the skin surface
(d) Subcutaneous fat
Ans-A layer of subcutaneous fat lies between the dermis and the underlying fascia. It helps to insulate the body from cold, cushions deep tissues from blunt trauma, and serves as a reserve source of energy for the body
(e) Arrector pili muscles
Ans- Arrector Pili Muscle – This is a tiny muscle that attaches to the base of a hair follicle at one end and to dermal tissue on the other end. In order to generate heat when the body is cold, the arrector pili muscles contract all at once, causing the hair to “stand up straight” on the skin.
(f) Stratum germinativum
Ans-The stratum germinatum (SG) provides the germinal cells necessary for the regeneration of the layers of the epidermis. These germinal cells are separated from the dermis by a thin layer of basement membrane
(g) Melanin
Ans- Melanin is the pigment that is responsible for our beautiful variety of skin tones and shades, eye colors, and hair colors. Not only does melanin provide pigmentation for human skin, hair, and eyes, it also provides protection against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) rays
Q-3. Answer the following questions briefly:
(a) Name the glands which are modification of sebaceous glands.
Ans- The meibomian gland is a modified lobulated sebaceous gland at the rim of the eyelid.
(b) Why is skin described as the jack of all trades?
Ans- Skin is called the jack of all trade because the skin is our body’s primary organ from which significant body functions such as sweating. Through sweat pores from our skin eliminate urea and excess salts such as NaCl from our body and many other functions
(c) Which glands are responsible for sweating?
Ans- Eccrine sweat glands are the most numerous, distributed across nearly the entire body surface area, and responsible for the highest volume of sweat excretion By contrast, apocrine and apo eccrine glands play a lesser role in overall sweat production as they are limited to specific regions of the body
(d) What is the basic difference between albinism and leukoderma?
Ans- The primary difference between the two is that vitiligo is an autoimmune disease that causes white patches on the skin, while albinism is a genetic disorder that causes the skin to appear very light all over the body, except in the case of partial albinism
(e) Under what conditions does piloerection occur?
Ans-Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose-pimples are the bumps on a person’s skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousal.
(f) What is the cause of albinism?
Ans-The cause of albinism is a defect in one of several genes that produce or distribute melanin, the pigment that gives skin, eyes, and hair their coloring. The defect may result in the absence of melanin production or a reduced amount of melanin production.
(g) How does skin in the human body help in storing food?
Ans-The deepest layer of skin can store water, fat, and metabolic products. Our body stores excess food in the form of fat in subcutaneous tissues(skin). Subcutaneous tissues not only store fat but also control body temperature
C. Long Answer Type Questions (Page 150)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
Q-1. Describe the mechanism that regulates sweating or perspiration?
Answer:–Secretion of sweat by eccrine glands in the skin. perspiration, in most mammals, water given off by the intact skin, either as vapour by simple evaporation from the epidermis (insensible perspiration) or as sweat, a form of cooling in which liquid actively secreted from sweat glands evaporates from the body surface
Q-2. Explain the terms vasodilatation and vasoconstriction. Discuss their role in regulating the body temperature.
Answer:–
Vasodilation: Dilation of blood vessels in the skin leading to an increase in the blood supply.
Vasoconstriction: Narrowing of blood vessels leading to reduction in the blood supply to the skin.
Temperature regulation in cold weather:
- At low temperature, the blood vessels get narrowed or vasoconstricted. This reduces the blood supply to the skin.
- There is less loss of heat by convection, conduction and radiation. There is less loss of heat through vaporization as reduced blood supply lowers the secretion of sweat by sweat glands.
Temperature regulation in hot weather:
- At high temperature, the blood supply to the skin is increased by vasodilation or dilation of blood vessels in the skin.
- This results in greater loss of heat by convection, conduction and radiation. There is more loss of heat through vapourization as more sweat is secreted due to rich supply of blood to the skin.
Q-3. Describe the structure of skin.
Answer: —The different layers of the skin include:
- Epidermis – The outermost layer that acts as a barrier
- Dermis – The middle layer comprising sweat glands, hair follicles and connective tissues
- Hypodermis – The innermost layer made of fat and connective tissues
D. Multiple Choice Questions MCQs (Page 150)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
Q-1. Which one of the following organs, actively functions in regulating our body temperature?
(a) Skin
(b) Heart
(c) Lung
(d) Stomach
Answer: (a) Skin
Q-2. What will happen if sebaceous glands in the body fail to function?
(a) Skin will turn darker with more melanin.
(b) Hairs will fail to grow.
(c) Skin will turn dry and rough.
(d) Body will not be able to regulate body temperature.
Answer: (c) Skin will turn dry and rough.
Q-3. Mammary glands are modified sweat glands which are
(a) Present in male
(b) Present in female
(c) Present in both male and female
(d) Absent in both
Answer: (b) Present in female
E Application /Skill-based Questions (Page 150)
(Ch-13 Skin-Structure and Functions Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions )
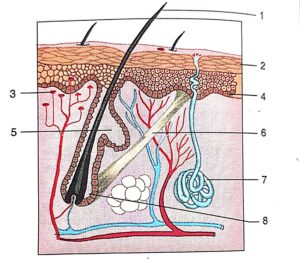
Look at the figure given here and answer the questions that follow:

(a) Label the parts marked 1-8
(b) Name the derivatives of skin.
(c) Give the role of structure marked by 3, 4, 5 and 7.
Answer:
(a) 1. Hair,2.Stratum corneum, 3. blood vessel 4.Stratum malpighian 5.Sebaceous gland 6.erector muscle, 7.Sweat gland 8. follicle
(b) The derivatives of the skin include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and mammary glands, hair, hair follicles, and nails. All are epidermal invaginations into the dermis. Sweat glands: Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous glands, are distributed over most of the body surface
(c) role of structure marked by
3.blood vessel – The blood vessels of the dermis provide nutrients to the skin and help regulate body temperature. Heat makes the blood vessels enlarge (dilate), allowing large amounts of blood to circulate near the skin surface, where the heat can be released
4.Stratum malpighian –Its role is vital as it protects the body (especially the underlying tissues) against pathogens and excessive water loss. It is also involved in providing insulation, temperature regulation and sensation. The human skin is made up of two layers, i.e. the epidermis and the dermis
5.Sebaceous gland ,–The normal function of sebaceous glands is to produce and secrete sebum, a group of complex oils including triglycerides and fatty acid breakdown products, wax esters, squalene, cholesterol esters and cholesterol. Sebum lubricates the skin to protect against friction and makes it more impervious to moisture.
7.Sweat gland—Sweat glands are used to regulate temperature and remove waste by secreting water, sodium salts, and nitrogenous waste (such as urea) onto the skin surface. The main electrolytes of sweat are sodium and chloride, though the amount is small enough to make sweat hypotonic at the skin surface
Thanks