Structure and Functions of Skin Goyal Brother Solutions ICSE Class-9 Biology Ch-15. We Provide Solutions of Exercise-15 Structure and Functions of Skin Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Ch-15. All Type exercise question such as name the following, difference between, MCQs, Answer the question. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Class-9 ICSE Biology Ch-15 Structure and Functions of Skin Goyal Brother Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brother Prakashan |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| Writer | Dr. S.K. Aggarwal |
| Chapter-15 | Structure and Functions of Skin |
| Topics | Solutions of Exercises-15 |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
Ch-15 Structure and Functions of Skin
Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
(Page-150)
Questions 1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) The three regions of skin epidermis are ..epidermis…. , ...dermis..… and .…hypodermis.….. .
(ii) Cells in the cornified layer are ..dead…. and are made up of ….keratin….. .
(iii) The melanin pigment is present in ..malpighian …. layer of ..epidermis…..
(iv) Dermis is made up of …connective….. tissue.
(v) Sweat glands are present in …skin…...
(vi) Warm-blooded animals are also called ..homeotherms…..
(vii) Cold-blooded animals are also called .ectothermy…. .
Questions 2. Choose the correct answer from the given options:
(i) The outermost protective covering of the body stretched all over the body is called
(a) Muscle
(b) Skin
(c) Skeleton
(ii) Which one of the following is not a derivative of human skin?
(a) Nails
(b) Hair
(c) Blood
(iii) Which of the following are able to maintain constant body temperature by generating body heat metabolically?
(a) Endotherms
(b) Ectotherms
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(iv) Modified sebaceous glands found in the auditory canal and secrete wax are
(a) Meibomian glands
(b) Ceruminous glands
(c) Subcutaneous glands
Questions 3. Define skin.
Answer : The skin is the body’s largest organ, made of water, protein, fats and minerals. Your skin protects your body from germs and regulates body temperature. Nerves in the skin help you feel sensations like hot and cold.
Questions 4. List the functions of skin.
Answer : Provides a protective barrier against mechanical, thermal and physical injury and hazardous substances. Prevents loss of moisture. Reduces harmful effects of UV radiation. Acts as a sensory organ (touch, detects temperature).
Questions 5. Name the two main layers of skin.
Answer : The epidermis and the dermis are the top two layers of skin in your body. The epidermis is the top layer, and the dermis is the middle layer. The dermis exists between the epidermis and the hypodermis. While the epidermis is the thinnest layer of skin, the dermis is the thickest layer of skin.
Questions 6. Name the three regions of skin epidermis.
Answer : It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. The skin’s structure is made up of an intricate network which serves as the body’s initial barrier against pathogens, UV light, and chemicals, and mechanical injury.
Questions 7. Name the pigment which imparts skin its colour.
Answer : Melanin is the pigment that gives human skin its colour.
Questions 8. Write, in brief, about the following
(i) Epidermis– Your epidermis is the outermost layer of skin on your body. It protects your body from harm, keeps your body hydrated, produces new skin cells and contains melanin, which determines the color of your skin
(ii) Dermis– The inner layer of the two main layers of the skin. The dermis has connective tissue, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, and other structures. It is made up of a thin upper layer called the papillary dermis, and a thick lower layer called the reticular dermis.
Questions 9. Mention the roles of the following:
(i) Blood capillaries– These tiny blood vessels have thin walls. Oxygen and nutrients from the blood can move through the walls and get into organs and tissues. The capillaries also take waste products away from your tissues. Capillaries are where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste.
(ii) Sweat glands– Sweat glands are used to regulate temperature and remove waste by secreting water, sodium salts, and nitrogenous waste (such as urea) onto the skin surface. The main electrolytes of sweat are sodium and chloride, though the amount is small enough to make sweat hypotonic at the skin surface.
Questions 10. What is keratin? Where is it found in the skin?
Answer : A type of protein found on epithelial cells, which line the inside and outside surfaces of the body. Keratins help form the tissues of the hair, nails, and the outer layer of the skin. They are also found on cells in the lining of organs, glands, and other parts of the body.
Questions 11. Write a short note on the derivatives of skin.
Answer : The derivatives of the skin include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and mammary glands, hair, hair follicles, and nails. All are epidermal invaginations into the dermis. Sweat glands: Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous glands, are distributed over most of the body surface.
Questions 12. Describe the role of skin in heat regulation.
Answer : The blood vessels of the dermis provide nutrients to the skin and help regulate body temperature. Heat makes the blood vessels enlarge (dilate), allowing large amounts of blood to circulate near the skin surface, where the heat can be released. Cold makes the blood vessels narrow (constrict), retaining the body’s heat.
Questions 13. Draw a labelled diagram of the vertical section of skin showing its structure.
Answer :
Questions 14. Observe the figure given below and answer the following questions:
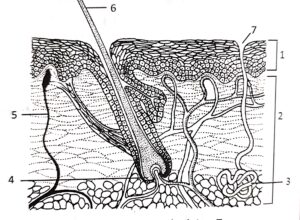
(i) Label the parts marked 1 – 7.
Answer 1 Epidermis 2- dermis 3- sweat gland 4- oil gland 5- hair follicle 6- hair 7- sensory neuron
(ii) State one function of each of the following:
Answer Part 2 dermis–Your dermis is the middle layer of skin in your body. It has many important functions, including protecting your body from the outside world, supporting your epidermis, feeling different sensations and producing sweat.
Part 3 sweat gland– The primary function of sweat glands is to keep the core body temperature at approximately 37 °C by releasing sweat in a hot environment or during physical activity.
Part 4 Oil gland– The normal function of sebaceous glands is to produce and secrete sebum, a group of complex oils including triglycerides and fatty acid breakdown products, wax esters, squalene, cholesterol esters and cholesterol. Sebum lubricates the skin to protect against friction and makes it more impervious to moisture.
(iii) In which of the part shown above is the brown pigment present?
Answer Malpighan Layer.
–: End of Structure and Functions of Skin Goyal Brother Solutions :–
Return to:- ICSE Biology for Class 9 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
thanks