Study of Gas Laws Exe-7 Structured Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-7. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-7 Study of Gas Laws with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Study of Gas Laws Exe-7 Structured Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-7 | Study of Gas Laws |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise – 7 Structured/Application Answer Type |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
E. Exercise – 7 Structured/Application Answer Type
Study of Gas Laws Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-133
Question 1.
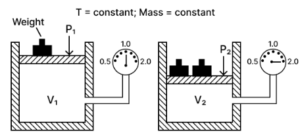
(a) State the law verified by the following figure:
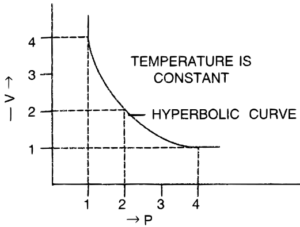
(b) Draw P.V. isothermal for the above law.
Answer:
(a) Boyle’s law — It states that the volume of a given mass of a dry gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature i.e., P1V1 = P2V2
(b) P.V. isothermal for Boyle’s law is shown below :
Question 2.
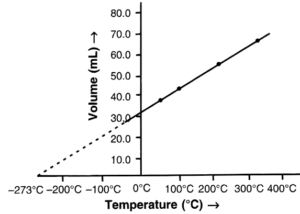
(a) State the law which the following graph verifies.
(b) Derive the mathematical expression for it.
(c) Give one application/use where the above law is employed.
Answer:
(a) Charles’ law — It states that pressure remaining constant, the volume of a given mass of dry gas increases or decreases by 1/273 of its volume at 0°C for each 1°C increase or decrease in temperature, respectively.
(b) Let V0 be the volume of a fixed mass of a gas at 0°C and let V be its volume at temperature t°C at constant pressure. Then according to Charles’ law,
V = Vo + (Vo/273)t (when P is constant)
V = Vo (1 + t/273)
= Vo (273 + t)/273
V =V0/273 T where T = 273 + t
For a given mass of a gas,
V0/273 = constant
∴ V = k x T (where k is constant)
or V α T and V/T = K
Suppose a gas occupies V1 cm3 at T1 temperature and V2 cm3 at T2 temperature, then by Charles law,
V1 α T1
or V1 = kT1 (k is constant)
or
V1/T1 = k and
V2 α T2
or V2/T2 = k
∴ V1/T1 = V2/T2 = k (at constant pressure)
(c) Volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, hence, density decreases with an increase in temperature. This is the reason that hot air is filled into balloons used for meteorological purposes.
Question 3.
Plot V versus absolute T (K) by the given data:
| Temperature | Volume in litres |
|---|---|
| 27°C | 4.8 |
| 77°C | 5.6 |
| 127°C | 6.4 |
| 177°C | 7.2 |
| 227°C | 8.0 |
(a) The graph between V and T is a …………… .
(b) Check whether the line passes through the origin.
(c) Which law is obeyed.
Answer:
Converting temperature to Kelvin Scale :
| Temp (°C) |
Temp (K) |
Volume (litres) |
|---|---|---|
| 27 | 300 | 4.8 |
| 77 | 350 | 5.6 |
| 127 | 400 | 6.4 |
| 177 | 450 | 7.2 |
| 227 | 500 | 8.0 |
Graph of V versus absolute T is shown below :
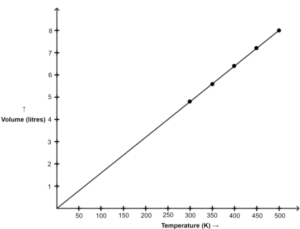
(a) The graph between V and T is a straight line.
(b) Yes, as we can see in the graph, the line passes through the origin.
(c) Charles’ law
— : End of Study of Gas Laws Exe-7 Structured Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends