Transpiration ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Solutions Chapter-5. We Provide Answer of Progress Check 1, 2, 3, 4, MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type Questions and Structured / Applications / Skill Type Questions of Exercise-5 Transpiration ICSE Class-10 Concise. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publishers PVT LTD |
| Subject | Concise Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | HS Vishnoi |
| Chapter-5 | Transpiration |
| Topics | Solutions of MCQs, Very Short ,Descriptive and Structural/Skill Questions and Progress Check 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Chapter 5 Transpiration Selina Biology Solution for ICSE Class 10
-: Select Topics :-
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE
D. LONG ANSWER TYPE
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE Transpiration Selina Concise for ICSE Class 10
Page 64-65
Question 1
Transpiration pull will be maximum under which set of the following conditions?
(a) Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
(b) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and well irrigated soil
(c) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and dry soil
(d) Closed stomata, dry atmosphere and dry soil
Answer 1
(a) Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
Question 2
With decrease in atmospheric pressure, the rate of transpiration will
(a) increase
(b) decrease rapidly
(c) decrease slowly
(d) remain the same
Answer 2
(a) increase
Question 3
One of the internal factors which affect the rate of transpiration, is
(a) big size of the leaf
(b) Colour of the leaf
(c) sunken stomata
(d) sunny day
Answer 3
(c) sunken stomata
Question 4
Guttation takes place through
(a) stomata
(b) lenticels
(c) lower epidermis of leaves
(d) hydathodes
Answer 4
(d) hydathodes
Question 5
Transpiration will be fastest when the day is
(a) cool, humid and windy
(b) hot, humid and still
(c) hot, humid and windy
(d) hot, dry and windy
Answer 5
(d) hot, dry and windy
Question 6
Most of the transpiration in tall trees occurs through
(a) Stomata
(b) Lenticels
(c) Cuticle
(d) Bark
Answer 6
(b) Lenticels
Question 7
Transpiration is best defined as
(a) loss of water by the plant
(b) evaporation of water from the aerial surfaces of a plant
(c) loss of water, as water vapour, by a plant
(d) release of water by a plant into the atmosphere
Answer 7
(b) evaporation of water from the aerial surfaces of a plant
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE ICSE Class 10 Transpiration
Page 65
Question 1
Name the following:
(a) Openings on the stem through which transpiration occurs
(b) The process by which the intact plant loses water in the form of droplets
(c) An instrument used to find the rate of transpiration
(d) A plant in which the stomata are sunken
(e) The apparatus to record the rate of transpiration in a cut shoot.
(f) Any two parts of a leaf which allow transpiration
(g) The structure in a leaf that allows guttation
(h) Loss of water as droplets from the margins of certain leaves.
Answer 1
(a) Lenticels
(b) Guttation
(c) Potometer
(d) Nerium
(e) Ganong’s photometer
(f) Stomata and cuticle
(g) Hydathodes
(h) Guttation
Question 2
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Transpiration is the loss of water as water ………… from the ………… parts of the plant.
(b) Closing of ………… and shedding of leaves reduce ………….
(c) Transpiration helps in creating …………. force and in eliminating excess ………….
Answer 2
(a) Transpiration is the loss of water as water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant.
(b) Closing of stomata and shedding of leaves reduce transpiration.
(c) Transpiration helps in creating suction force and in eliminating excess water.
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE Transpiration Selina Biology Solution for ICSE Class 10
Page 65
Question 1
Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
chloroplasts and photosynthesis
In a similar way, write the functional activity against each of the following:
(a) Hydathodes and ………………………………
(b) Leaf spines and ………………………………
(c) Lenticels and ………………………………….
(d) Xylem and ……………………………..
Answer 1
(a) guttation
(b) protection and reduced transpiration
(c) transpiration
(d) conduction of water and mineral salts
Question 2
(a) State whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F)?
(i) Most transpiration occurs at midnight.
(ii) Transpiration creates a pull for the upward movement of the sap.
(iii) Wind velocity has an effect on transpiration.
(iv) Atmospheric humidity promotes transpiration from a green plant.
(v) Transpiration helps to cool the body of the plant.
(b) Rewrite the false statements in (a) above, in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Answer 2
(i) False. Most transpiration occurs at mid-day.
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False. Transpiration is reduced if the air outside is humid.
(v) False. Perspiration and transpiration help to cool the body temperature of the organism
Question 3
Give suitable explanation for the following :
(a) A higher rate of transpiration is recorded on a windy day rather than on a calm day.
(b) Excessive transpiration results in the wilting of the leaves.
(c) Some plants show wilting of their leaves at noon even when the soil is well-watered.
(d) More transpiration occurs from the lower surface of a dorsiventral leaf.
(e) The stomata in most plants are more numerous on the lower surface of a leaf as compared to the upper surface.
(f) Forests tend to bring more rains.
(g) On a bright sunny day, the leaves of certain plants roll up.
Answer 3
(a) Transpiration increases with the velocity of wind. If the wind blows faster, the water vapours released during transpiration are removed faster and the area surrounding the transpiring leaf does not get saturated with water vapour.
(b) When the rate of transpiration far exceeds the rate of absorption of water by roots, the cells lose their turgidity. Hence, excessive transpiration results in wilting of the leaves.
(c) During noon the rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of absorption of water by roots. Due to the excessive transpiration, the cells of leaves lose their turgidity and wilt.
(d) There are more stomatal openings on the lower surface of a dorsiventral leaf. More the number of stomata, higher is the rate of transpiration. Hence more transpiration occurs from the lower surface.
(e) The lower surface of leaf is sheltered from direct sunlight. If more stomata are on the upper surface of a leaf, then excessive transpiration would occur, resulting in quick wilting of the plant. Hence most plants have more numerous stomata on the lower surface of a leaf to control the rate of transpiration.
(f) Plants lose water in the form of water every day into the atmosphere through transpiration. A tree loses more than 30 litres of water per day. Hence a huge amount of water is escaped into the atmosphere by forests. This increases the moisture in the atmosphere and brings more frequent rains.
(g) On a bright sunny day, the rate of transpiration is much higher than any other days. The leaves of certain plants roll up on a bright sunny day to reduce the exposed surface and thus reduce the rate of transpiration.
D. LONG ANSWER TYPE Transpiration Concise Biology Solutions for ICSE Class 10
Page 65-66
Question 1
Define the following terms :
(a) Transpiration
(b) Exudation
(c) Potometer
(d) Wilting
(e) Hydathodes
(f) Cuticle
Answer 1
(a) Transpiration : Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism.
(b) Exudation : An exudate is a bodily fluid that oozes out or is discharged from the tissues during inflammation. The fluid exudes out via the pores or a wound. It may be cloudy or pus-like. It contains exudate cells (e.g. white blood cells), serum, and fibrin.
(c) Potometer : A potometer, sometimes known as a transpirometer, is a device used for measuring the rate of water uptake/intake of a leafy shoot which is almost equal to the water lost through transpiration.
(d) Wilting : Wilting is the loss of rigidity of non-woody parts of plants.
(e) Hydathodes : A specialized pore on the leaves of higher plants that functions in the exudation of water.
(f) Cuticle : Cuticle is a water-impervious protective layer covering the epidermal cells of leaves and other parts and limiting water loss.
Question 2
Distinguish between the following pairs :
(a) Stomata and lenticels
(b) Guttation and bleeding
(c) Transpiration and Evaporation
Answer 2
(a) Stomata and lenticels :
| Stomata | lenticels |
| 1. Stomata are the minute opening mainly present on leaves. | 1. Lenticels are found in the bark of woody stems. |
| 2. Stomata can be open and closed. | 2. These are always opened. |
| 3. These are located on the lower surface of dicot leaves and both upper and lower surfaces of monocot leaves. | 3. These are located on the stems of woody plants. |
| 4. They lose water vapour and the process is termed stomatal transpiration. | 4. They lose water vapour and the process is called lenticular transpiration. |
(b) Guttation and bleeding :
| Guttation | Bleeding |
| It is the removal of excess water from the plants because of excess water buildup in the plant. | It is the removal of water from the plant because of injury. |
| Water escapes from specialised structures called hydathodes. | Water escapes in the form of sap from the injured part of the plant. |
| It occurs from edges of leaves. | It occurs from cuts found in plants. |
(c) Transpiration and Evaporation :
| Transpiration | Evaporation |
| It is a biological process. | It is a physical process. |
| Transpiration is a slow process. | Comparatively a fast process. |
| Occurs in living tissues. | Involves non-living matter. |
| In the process of transpiration water is lost from plant cells | In this process, water is lost from the surface of plant parts |
Question 3
Suppose you have a small rose plant growing in a pot. How would you demonstrate transpiration in it?
Answer 3
Take the small potted rose plant and cover it with a transparent polythene bag. Tie its mouth around the base of the stem. Leave the plant in sunlight for an hour or two.

Drops of water will soon appear on the inner side of the bag due to the saturation of water vapour given out by the leaves. A similar empty polythene bag with its mouth tied and kept in sunlight will show no drops of water. This is the control to show that plants transpire water in the form of water. If tested with dry cobalt chloride paper, the drops will be confirmed as water only.
Question 4
What is lenticular transpiration? Mention one major difference between lenticular transpiration and stomatal transpiration.
Answer 4
Transpiration occurring through lenticels i.e. minute openings on the surface of old stems is called lenticular transpiration.
Stomatal transpiration is controlled by the plant by altering the size of the stoma, where as this does not happen in case of lenticular transpiration. This is because the lenticels never close, but remain open all the time.
The amount of stomatal transpiration is much more than the amount of lenticular transpiration.
Question 5
Droplets of water may sometimes be seen along the margins of the leaves of a banana plant, growing in wet soil in the mornings. Are these dew drops? Comment upon your answer.
Answer 5
No, they are not dew drops.
This is water given out by the plant body through guttation. Since the banana plant is growing in humid environment, transpiration is hampered. But the roots continue to absorb water from the soil. This builds up a huge hydrostatic pressure within the plant and forces out the excess water from the hydathodes, which are pores present at the tips of veins in the leaf. This is observed especially during the mornings.
Question 6
Briefly explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by:
(a) Intensity of light
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere
(c) Temperature.
Answer 6
(a) Intensity of light – During the day, the stomata are open to facilitate the inward diffusion of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. At night they are closed. Hence more transpiration occurs during the day. During cloudy days, the stomata are partially closed and the transpiration is reduced.
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere – When the air is humid; it can receive very less water vapour. Thus, high humidity in the air reduces the rate of outward diffusion of the internal water vapour across stomata, thereby reducing the rate of transpiration.
(c) Temperature – Transpiration rates go up as the temperature goes up, especially during the growing season, when the air is warmer due to stronger sunlight and warmer air masses.
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE Transpiration Selina Concise Biology Solution for ICSE Class 10 Chapter 5
Page 66-67
Question 1
The give figure represent an experiment :
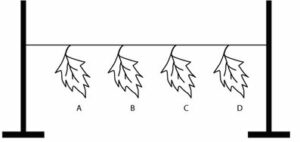
(a) Leaf A was coated with grease on both the surfaces.
(b) Leaf B was coated with grease on the lower surfaces.
(c) Leaf C was coated with grease on the upper surfaces.
(d) Leaf D was left without any application of grese.
All the four leaves A, B, C, D were left in a room for 24 hours.
(i Which leaf dries first ? Give reason
(ii) Which leaf dries last ? Give reason.)
Answer 1
(i) Leaf D: i.e. the leaf with no greasing on either surfaces would dry first because it would lose water from both surfaces i.e. it would lose maximum quantity of water.
(ii) Leaf A: which was coated with grease on both the surfaces would dry last because greasing prevents evaporation of water and transpiration occurs through stomata which are present more on the lower surface of the leaf.
Question 2
Given below is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:
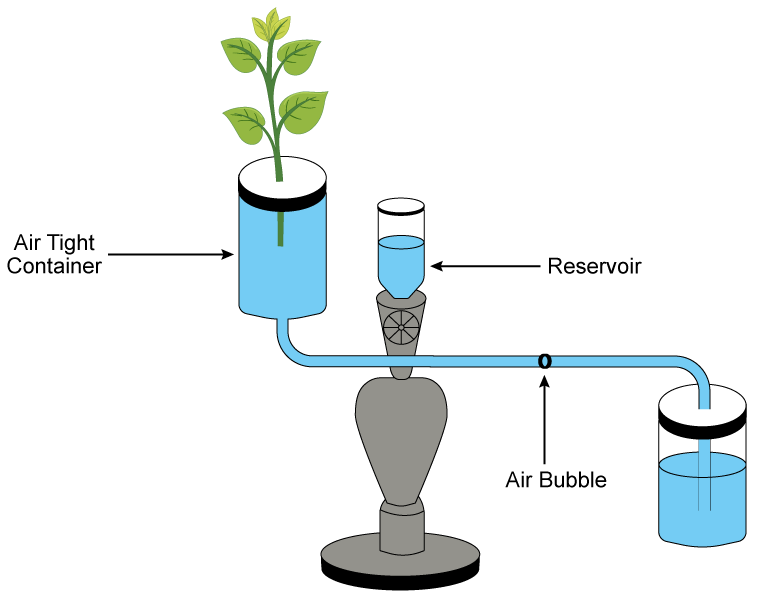
(a) Name the apparatus.
(b) What is it used for?
(c) What is the role played by the air-bubble in this experiment?
(d) What is the use of the reservoir?
(e) What happens to the movement of the air-bubble if the apparatus is kept:
(i) In the dark
(ii) In sunlight
(iii) In front of a fan
Give a reason in each case.
Answer 2
(a) Ganong’s potometer
(b) Ganong’s potometer is used to measure the water intake of a plant which is almost equal to the water lost through transpiration.
(c) The movement of the air bubble and its position in the capillary tube indicates the volume of water lost through transpiration in a given time.
(d) The water in the reservoir can be released into the capillary tube by opening the stop cock. This allows the air bubble to restore back to its original position.
(e)
(i) If the apparatus is kept in the dark, there will be no transpiration as the stomata would be closed. As a result, there would be no movement of the air bubble and it would remain stable.
(ii) If the apparatus is kept in bright sunlight, the rate of transpiration will be more. As a result, the movement of the air bubble would be larger since there would be more loss of water due to transpiration.
(iii) If the apparatus is kept in front of a fan, the rate of transpiration will be more. As a result, the movement of the air bubble would be larger since there would be more loss of water due to transpiration as the velocity of wind/air increases.
Question 3
Given ahead is the diagram of an experimental set up to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
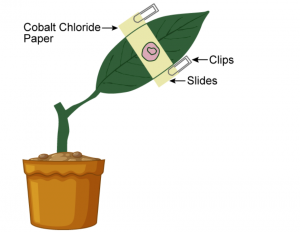
(a) Name the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper.
(b) Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
(c) Why are glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
(d) After about half an hour what change, if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper placed on the dorsal and ventral sides of the leaf? Give a reason to support your answer.
Answer 3
(a) Blue.
(b) The experimental leaf is a dicot leaf as it shows reticulate venation and there are more number of stomatal openings on the undersurface of a dicot leaf. Hence, transpiration is more and can be easily observed.
(c) Glass slides are placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers so as to retain the strips in their position.
(d) The cobalt chloride paper on the dorsal side will turn less pink or turns pink in a much longer time; while the one on the ventral side will turn more pink. This occurs because the ventral surface has more number of stomata as compared to the dorsal surface. As a result, the rate of transpiration is more on the ventral side than on the dorsal side of a dicot leaf.
Question 4
An outline sketch of a tree is shown in a diagram below. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
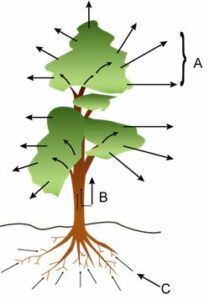
(a) Name and define the phenomenon labelled A in the diagram.
(b) Write the significance of the process mentioned in A for the plants.
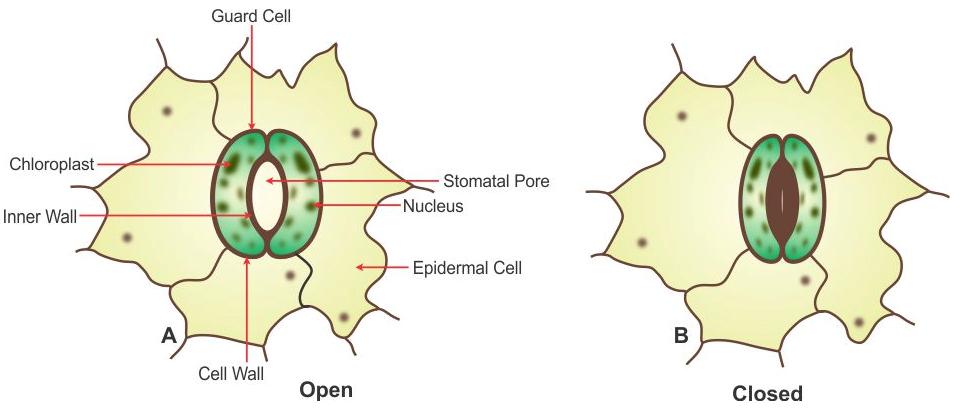
(c) What do the direction of arrows in B and C indicate? Name the phenomenon.
(d) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of an opened stomata.
Answer 4
(a) A is transpiration. Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water from the aerial parts (leaves and stem) of the plants.
(b) Significance of transpiration for the plant :
- Cooling effect
- Suction force
- Distribution of water and minerals
(c) Arrow B indicates water passing up the trunk and the phenomenon is lenticular transpiration/ascent of sap. Arrow C indicates water absorbed by roots from the soil and the phenomenon is called endosmosis.
(d) opened stomata :
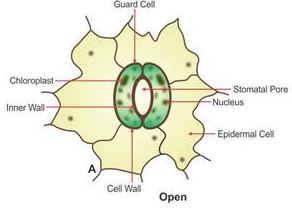
Question 5
The figure given below represents an experimental setup with a weighing machine to demonstrate a particular process in plants. The experimental setup was placed in bright sunlight. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
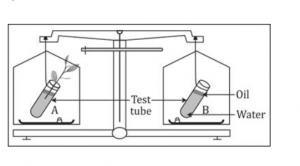
(a) Name the process intended for study.
(b) Define the above mentioned process.
(c) When the weight of the test tubes A and B is taken before and after the experiment, what change is observed? Justify.
(d) What is the purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental setup.
(e) What is the purpose of putting oil in the test tube.
Answer 5
(a) Transpiration
(b) Transpiration is a process by which water is lost in the form of water vapour from aerial parts of the plant.
(c) Weight of test tube A before the experiment was more than its weight after the experiment. This is because water from test tube A has evaporated due to transpiration.
Weight of test tube B remains the same before and after the experiment, because no loss of water occurs in test tube B.
(d) Test tube B is used here as a control. This makes the observation of the change in test tube A easy.
(e) Oil is stops water evaporation from surface.
Question 6
An apparatus as shown below was set up to investigate a physiological process in plants. The setup was kept in sunlight for two hours. Droplets of water were then seen inside the bell jar. Answer the questions that follow:
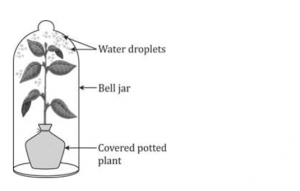
(a) Name the process being studied.
(b) Explain the process named above in (a).
(c) Why was the pot covered with a plastic sheet?
(d) Suggest a suitable control for this experiment.
(e) Mention two ways in which this process is beneficial to plants.
(f) List three adaptations in plants to reduce the above mentioned process.
Answer 6
(a) Transpiration
(b) Transpiration is a process during which water is lost in the form of water vapour through aerial parts of the plant.
(c) The pot is covered with a plastic sheet to prevent evaporation of water from the soil.
(d) A control for this experiment will be an empty polythene bag with its mouth tied.
(e) Transpiration is beneficial to plants in the following ways:
- It creates a suction force in the stem which enables the roots to absorb water and minerals.
- It helps in cooling the plant in hot weather.
(f) Adaptations in plants to reduce transpiration are
- Leaves may be modified into spines as in cactus or into needles as in pines.
- The number of stomata is reduced and they may be sunken in pits.
- Leaves may be folded or rolled up.
Question 7
The apparatus shown in the following diagram is Garreau’s potometer designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.
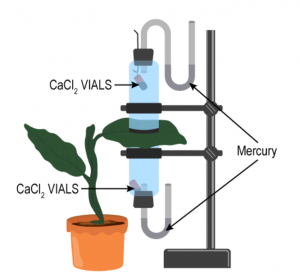
(a) What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
(b) After few hours CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight? If so, give reason.
(c) What is the purpose of using a manometer?
(d) What do you mean by transpiration?
Answer 7
(a) CaCl2 is a hygroscopic compound that absorbs moisture/water without changing its state. CaCl2 vials inside the cup to absorb water.
(b) Yes, after few hours the weight of the CaCl2 vials will increase because they will absorb water lost by the leaf of the plant due to transpiration.
(c) Manometer is used to measure the pressure. In order to measure the pressure exerted by the fluid, the fluid is allowed to exert pressure on one of the closed ends of the tube. Under the effect of the pressure, the liquid inside the manometer tube gets displaced and the amount of displaced liquid is measured.
(d) Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts (leaves and stem) of the plant.
Return to Concise Selina ICSE Biology Class-10
Thanks