Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan Chapter-23 Solutions. We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-23 Properties of Mensuration for ICSE Class-7 RS Aggarwal Mathematics.
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-23 A, Exe-23 A, Exe-23 B, Exe-23 C, Exe-23 D, Exe-23 E, Exe-23 F, Exe-23 G and MCQs Exe-23 H, with Mental Maths to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-7 Mathematics.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal brothers Prakshan |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 7th |
| Chapter-23 | Mensuration |
| Writer | RS Aggrawal |
| Book Name | Foundation |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-23 A, Exe-23 A, Exe-23 B, Exe-23 C, Exe-23 D, Exe-23 E, Exe-23 F, Exe-23 G and MCQs Exe-23 H, with Mental Maths to develop skill and confidence |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan Chapter-23 Solutions
-: Select Topic :-
Mensuration is the branch of Mathematics that studies the measurement of the geometric figures and their parameters like length, volume, shape, surface area, lateral surface area, etc.
Mensuration Formulas: Area Formulas & Perimeter Formulas
Before getting into the list of Mensuration formulas, i.e. area formulas and perimeter formulas of all major geometric shapes, let’s have a look at the definition of ‘area’ and ‘perimeter
What Is Area Of A Geometric Figure?
The area of a closed geometric figure is basically the size or extent of the two-dimensional surface of the figure
What Is Perimeter Of A Geometric Figure?
The perimeter of a closed geometric figure is the total length of the boundary of the figure.
Mensuration :- Important Unit related 2D
| Terms | Abbreviation | Unit | Definition |
| Area | A | m2 or cm2 | The area is the surface which is covered by the closed shape. |
| Perimeter | P | cm or m | The measure of the continuous line along the boundary of the given figure is called a Perimeter. |
| Volume | V | cm3 or m3 | The space occupied by a 3D shape is called a Volume. |
| Curved Surface Area | CSA | m2 or cm2 | If there’s a curved surface, then the total area is called a Curved Surface area. Example: Sphere |
| Lateral Surface area | LSA | m2 or cm2 | The total area of all the lateral surfaces that surrounds the given figure is called the Lateral Surface area. |
| Total Surface Area | TSA | m2 or cm2 | The sum of all the curved and lateral surface areas is called the Total Surface area. |
| Square Unit | – | m2 or cm2 | The area covered by a square of side one unit is called a Square unit. |
| Cube Unit | – | m3 or cm3 | The volume occupied by a cube of one side one unit |
Area Formulas Of Common Geometric Figures
| Geometrical Shapes | Area Formulas | Variables |
| Area of Square | Area = a x a = a2 | a = Length of each side of the square |
| Area of Rectangle | Area = l x b | l = Length of the rectangle b = Breadth of the rectangle |
| Area of Triangle | Area = (b x h)/2 | b = Length of the base of the triangle h = Height of the triangle |
| Area of Circle | πr2 | π = 22/7 = 3.14159 (approx) r = Radius of the circle |
| Area of Parallelogram | Area = b x h | b = Base of the parallelogram h = Height of the parallelogram |
| Area of Trapezium | Area = {(a + b) x h}/2 | a + b= Sum of the lengths of the two parallel sides of the trapezoid, i.e. Base 1 and Base 2 h = Perpendicular distance between the two parallel sides |
| Area of Rhombus | Area = (p x q)/2 | p = Length of 1st diagonal q = Length of second diagonal pq = Product of the two diagonals |
| Area of Ellipse | Area = πab | a = Major radius b = Minor radius |
Perimeter Formulas Of Common Geometrical Figures
| Geometrical Shapes | Perimeter Formulas | Variables |
| Perimeter of Square | Perimeter = 4a | a = Length of each side of the square |
| Perimeter of Rectangle | Perimeter = 2 (l + b) | l = Length of the rectangle b = Breadth of the rectangle |
| Perimeter of Triangle | Perimeter = a + b + c | a, b and c are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle |
| Perimeter of Circle | Perimeter = πd = 2πr | π = 22/7 = 3.14159 (approx) r = Radius of the circle d = Diameter of the circle |
| Perimeter of Parallelogram | Perimeter = 2 (l + b) | l = Length of the parallelogram b = Breadth of the parallelogram |
| Perimeter of Trapezium | Perimeter = a + b + c + d | a, b, c, d are the lengths of the four sides of the trapezoid |
| Perimeter of Rhombus | Perimeter = 4a | a = Length of each side of the rhombus |
| Perimeter of Kite | Perimeter= 2a + 2b | a = Length of each side of the first pair b = Length of each side of the second pair |
Additional Area And Parameter Formulas
Some additional formulas to calculate area and perimeters are as under:
| Area of a Triangle of Given Sides – a, b, c | Area = √ [s (s – a) (s – b) (s – c)] | s = Semi-perimeter of the triangle = (a + b + c)/2 |
| Area of an Isosceles Triangle | Area = (base x height)/2 base = b height = √(a2 − b2/4) |
a = Length of each of the equal sides of the isosceles triangle b = Length of the base |
| Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle | Perimeter = 2a + b | a = Length of each of the equal sides of the isosceles triangle b = Length of the base |
| Area of an Equilateral Triangle | Area = (√3 x a2)/4 | a = Length of each side of the equilateral triangle |
| Perimeter of an Equilateral Triangle | Perimeter = 3a | a = Length of each side of the equilateral triangle |
| Perimeter of a Semi-Circle | Perimeter = πr + d = 3πr | r = Radius of the circle d = 2r = Diameter of the circle |
| Area of a Semi-Circle | Area = (πr2) x (1/2) | r = Radius of the circle |
Exe-23 A,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 247
Question 1:
Find the perimeters of :
(i)………….
…………….
Question 2:
………………………
…………………….
……………………..
Question 11:
The wheel of a car rotated 1000 times in travelling a distance of 1.76 km. Find the radius of the wheel.
Exe-23 B,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 250
Question 1:
Find the area of each of the figure drawn on the unit ……………….. has side 1 cm.
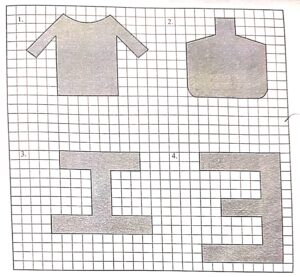
Answer :
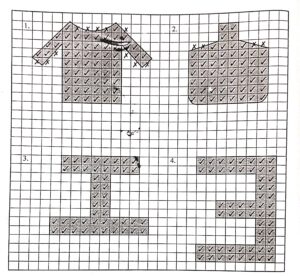
1.Shirt
(i)Place the shirt on the square grid sheet , as shown in the figure.
(ii) Draw it’s outer boundary using a sharp pencil , as shown in the figure .
(iii)Remove the shirt.
(iv)Mark(right) each one of the complete squares lying within the boundary of the shirt .
(v)Mark(right) each one of the squares lying either half or more than half within the boundary of the shirt .
(vi) Mark(wrong) each of the squares lying less than half within the boundary of the shirt .
(vii)Count all the squares marked (right) and neglect all the squares marked (wrong) or unmarked .
(viii)The counted squares give the area of the shirt in sq. cm.Here the area of the shirt is 60 \( cm^{2} \)
2. Bottle
(i) Place the bottle on the unit square grid sheet ,as shown in the figure.
(ii)Draw its outer boundary using a sharp pencil,as shown in the figure.
(iii)Remove the bottle.
(iv)Mark (right) each one of the complete squares lying within the boundary of the bottle.
(v)Mark (right) each one of the squares lying lying either half or more than half within the boundary of the bottle.
(vi)Mark(wrong) each of the squares lying less than half within the boundary of the bottle .
(vii)Count all the squares marked (right) and neglect all the squares marked (wrong) or unmarked .
(viii) The counted square give the area of the bottle in sq. cm. Here , the area of the bottle is 56 \( cm^{2} \).
3- Alphabet- 1
(i) Place the alphabet – I on the unit square grid sheet ,as shown in the figure .
(ii) Draw it’s outer boundary using a sharp pencil , as shown in the figure .
(iii) Remove the Alphabet -I.
(iv)Mark (right) each one of the complete squares lying within the boundary of the Alphabet -I.
(v)Mark (right) each one of the squares lying lying either half or more than half within the boundary of the Alphabet -I.
(vi))Mark(wrong) each of the squares lying less than half within the boundary of the Alphabet -I.
(vii)Count all the squares marked (right) and neglect all the squares marked (wrong) or unmarked .
(viii)The counted squares give the area of the Alphabet -I. in sq. cm. Here , the area of the Alphabet -I. is 46 \( cm^{2} \).
4. Inverted E
(i)Place the inverted E on the unit square grid sheet ,as shown in the figure .
(ii)Draw it’s outer boundary using a sharp pencil , as shown in the figure .
(iii)Remove the inverted E.
(iv)Mark (right) each one of the complete squares lying within the boundary of the inverted E.
(v)Mark (right) each one of the squares lying lying either half or more than half within the boundary of the inverted E.
(vi)Mark(wrong) each of the squares lying less than half within the boundary of the inverted E.
(vii)Count all the squares marked (right) and neglect all the squares marked (wrong) or unmarked .
(viii)The counted squares give the area of the Alphabet -I. in sq. cm. Here , the area of the inverted E. is 56 \( cm^{2} \).
Exe-23 C,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 255
Question 1:
Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle having :
(i)……………….
…………………..
Question 2:
……………………..
……………………..
………………………
Question 12:
Find the area and perimeter of the …………….. following figures
…………….
Exe-23 D,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 258
Question 1:
A room is 10 m long …………….. 236 per m².
Question 2:
………………………
………………………
………………………
Question 8:
Find the area of the shaded region in each of the following figure :
Exe-23 E,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 261-262
Question 1:
Find the area of the triangle, having :
‘(i)…………
…………………
Question 2:
……………………..
………………………
………………………
Question 18:
Find the area ………………….. DA = 48 cm.
Exe-23 F,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 265-266
Question 1:
Find the area of the parallelogram having :
(i)………………
…………………..
Question 2:
…………………….
./……………………
……………………….
Question 11:
Find the area of the shaded region of each of the figure :
Exe-23 G
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 268
Question 1:
Find the area of a circle whose radius is :
(i) 2.8 m
(ii) 8.4 m
Question 2:
…………………….
……………………..
……………………….
Question 14:
The area of a circle garden ……………………… 2002 m² find :
(i)………………..
………………..
MCQs Exe-23 H,
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 268-269
Choose the correct option in each of the following
Question 1:
The length of the diagonal ……………… b unit is .
…………………..
Question 2:
………………………
……………………….
………………………
Question 15:
The area of a ……………. is equal to
………………….
Mental Maths
Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal ICSE Goyal Brother Prakashan
Page 269
1. Fill in the blanks :
(i)The perimeter of a simple closed figure is the length of it’s Boundary.
(ii)The Perimeter of a circle is called it’s circumference.
(iii)Pie (π ) is the ratio of the circumference of any circle to it’s diameter.
(iv)The area of a simple closed figure is the measure of the surface enclosed by it
(v)An area of 1 hectare is equal to 10000\( m^{2} \).
(vi) A unit square grid sheet is a sheet containing horizontal and vertical lines forming squares , each of dimensions 1 cm*1 cm.
(vii) In a triangle having lengths a units , b units and c units respectively , if s=\( \frac{a+b+c}{2} \)units, then s is called the semi perimeter of the triangle.
(viii)The area of a Triangle ABC having BE ⊥ AC,is \( \frac{1}{2}AC*BE sq.units \).
(ix)Area of a right triangle is equal to \( \frac{1}{2} \)Base *Height.
(x)Area of a triangle having sides of lengths a units , b units and c units respectively and semiperimeter s unit is \( \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \)sq.units.
(x) The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of the length of side and the corresponding height.
(xi) Area of a rhombus is equal to \( \frac{1}{2} \)* Product of diagonals.
(xii)The Region enclosed between two concentric circles of different radii is called a ring.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is mensuration in Maths?
In maths, mensuration is defined as the study of the measurement of various 2D and 3D geometric shapes involving their surface areas, volumes, etc.
What is the formula for mensuration?
Mensuration is commonly referred to as the study of geometry and the formulas that come under it involve the calculation of Area, Perimeter of different types of figures. For a list of formulas, you can refer to this article
What is the difference between mensuration and geometry?
Mensuration refers to the calculation of various parameters of shapes like the perimeter, area, volume, etc. whereas, geometry deals with the study of properties and relations of points and lines of various shapes.
How can we remember mensuration formulas?
Ans: The best way to remember mensuration formulas would be by understanding area and perimeter concepts and then you can use the formula tables provided in this article. You can either take a printout of the page or bookmark it whenever you need it
Where can I get RS Aggarwal Mensurations Solutions Goyal Brother Prakashan
you can get RS Aggarwal Mensuration Solutions of Goyal Brother Prakashan for class-7 at www.icsehelp.com Get free solutions of all Chapter of RS Aggarwal Goyal Brothers.
–: End of Mensuration Class-7 RS Aggarwal Solutions :–
Return to- RS Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-7 Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Thanks





This link works only once… Now From 1 month I am not able to open this tab…
our any content is not protected, currently unavailable, hence the uploading solution work is in progress
Why the answers not visible
It has been removed and will be uploaded soon
will be visible
When sir answer will be visible ..kids are facing difficulties in some questions ..their exam are coming plz sir upload answer ..asap
ok very soon we are working day and night to resolve the issue
Sir when u will puy answers ..we really neee this chapter solution
within a weak
I want Ex 23 D
uploaded
I am not able to open exercise 23 D
23 d working properly please visit page 2 or 3 having option at bottom of page-1