Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified ICSE Class-10 Solutions Chapter 9:- Solutions of Dr Dalal Simplified ICSE Chapter-9 Practical Chemistry by Dr Viraf and J Dalal for Class 10. Step by step Solutions of Dr Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry by Dr Viraf and J Dalal of Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified .
Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified ICSE Class-10
Get Other Chapter Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Class-10 Solutions
How to Solve Mole Concept ICSE Chemistry Class-10
Note:– Before viewing Solutions of Practical Chemistry by Dr Viraf and J Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions of Chapter-9 .Read the Chapter-4 Practical Chemistry Carefully to understand the concept in better way .After reading the Chapter-9 Practical Chemistry solve all example of your text book with ICSE Specimen Sample Paper for Class-10 Exam of Council. Focus on Practical Chemistry is the Most important Chapter in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry.Previous Year Solved Question Paper for ICSE Board
Additional Questions Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified
Question 1.
The following materials are provided – solutions of cobalt chloride, ammonia, potassium permanganate, lime water, starch-iodide, sodium hydroxide, lead acetate, potassium iodide. Also provided are litmus and filter papers, glowing splinters and glass rods. Using the above how would you distinguish between :
(a) a neutral, acidic and a basic gas
(b) oxygen and hydrogen gas
(c) carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide gas
(d) chlorine and hydrogen chloride gas
(e) hydrogen sulphide and nitrogen dioxide gas
(f) ammonia and carbon dioxide gas
(g) zinc carbonate and potassium nitrate
(h) hydrated copper sulphate and anhydrous copper sulphate
(i) ammonium sulphate and sodium sulphate.
Answer:
(a) Neutral gas does not effect litmus paper. Acidic gas turns blue litmus paper red and basic gas turns red litmus blue.
(b) Oxygen is obtained by heating KMNO4 whereas hydrogen gas is obtained with the action of Zn and dil H2SO4.
(c) No effect of CO2 on KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 whereas SO2 turns K2Cr2O7 from orange to green.
(d) Chlorine decolourises the colouring matter whereas HCl does not.
(e) H2S gas turns KMnO4 from pink to colourless and NO2 liberates violet vapours with KI.
(f) NH3 turns red litmus blue and S02 turns blue litmus red.
(g) Lime water turns zinc carbonate milky and no effect on potassium nitrate.
(h) Hydrated copper sulphate anhydrous copper sulphate. Take some dry CuSO4 on filter paper. It will be white in colour.
anhydrous copper sulphate white in colour. CuSO4 (white powder)
Now keep it in air for some time, it will absorb water vapous from atmosphers, its colour will change to blue.
(i) Ammonium sulphate and sodium sulphate : When ammonium sulphate is heated with NaOH, gas ammonia is producedwhich turns red litmus blue. But sodium sulphate has no reaction with NaOH.
Question 2.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between the following:
- Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphate
- Potassium chloride and potassium nitrate
- Copper carbonate and copper sulphite
- Lead chloride and lead sulphide
- Iron (II) sulphate and iron (III) sulphate
- Calcium sulphate and zinc sulphate
- Lead nitrate and zinc nitrate
- Copper sulphate and calcium sulphate
- Manganese dioxide and copper (II) oxide
- dil. HCl, dil. HNO3, dil. H2SO4.
[explain the procedure for the preparation of the solutions for the above tests wherever required]
Answer:
(i) Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphate : Add BaCl2 solution to Na2CO3,a white precipitates produced which are soluble in dil. HCl.
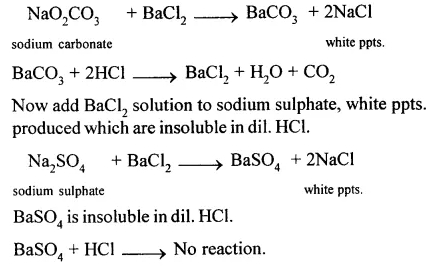
(ii) Add cone. H2SO4 to potassium chloride and heat.
colourless gas produced which gives dense-white fumes when a glass rod dipped in ammonia is brought near it.
To the salt solution potassium nitrate, add cone. H2SO4 and copper turnings and heat.
Reddish brown fumes evolved which gives violvet vapours and turns potassium iodide paper brown.
(iii) On adding dilute H2SO4 to copper carbonate acid heating, a colorless odour less gas is evolved which turns lime water milky and has no effect on KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 solution.![]()
CO2 gas turns lime water milky.
Now add dil. H2SO4 to copper sulphite and heat.
A colourless gas with suffocating odour evolved which turns lime water milky and changes then pink colour of acidified KMnO4 to colourless and orange colour of acidified K2Cr2O7 to clear green.
(iv) Added MnO2 and cone. H2SO4 to the salt Lead Chloride and heat it.
A greenish coloured yellow coloured gas with punget odour is evolved which turns moist starch iodide paper blue black.
Now add dil. H2SO4 to Lead sulphide and heat.
Colourless gas with rotten egg smell is evolved. The gas evolved turns moist lead acetate paper silvery black.
(v) Iron (II) sulphate is when reacted with small amount of NaOH solution, dirty green precipitates of Iron (II) hydroxide are produced which are insoluble in excess of NaOH.

Iron (III) sulphate is when reacted with small amount of NaOH solution, reddish brown precipitates of Fe(OH)3 are formed which are insoluble in excess of NaOH.
(vi) Add sol. of NaOH to calcium sulphate solution, milky white ppts. of calcium hydroxide are formed which are soluble in excess of NaOH.
Now add NaOH to zinc sulphate a white ppts of Zn(OH)2 are produced which are soluble in excess of NaOH.
Also when sol. of NH4OH is add to CaSO4, no ppts. are formed i. e., no reaction whereas when a sol. of NH4OH is add to ZnSO4, gelatinous white ppts. are formed which are soluble is excess of NH4OH.
(vii) When a sol. of NH4OH in small amount is added to lead nitrate sol. a chalky white precipitates of lead hydroxide are produced. The precipitats so formed are unsoluble in excess of NH4OH.
Now add NH4(OH) in small amount to zinc nitrate, a Gelatinous white precipitates of Zn(OH)2 are formed which are soluble in excess of NH4OH.
(viii) When a sol. of NaOH in small amount is added to copper sulphate, pale blue precipitates of copper (II) hydroxide are formed which are insoluble in excess of NaOH.
Now add sol. of NaOH to calcium sulphate sol. milky white ppts. of Ca(OH)2 are formed which are insoluble in excess of NaOH.
(ix) Test : (i) Add cone. HCl to the sol. and heat, (ii) Filter the sol. after reaction.
Manganese dioxide (Black) : Greenish coloured gas is evolved MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 Filterate is brownish in colour.
Copper (II) oxide : There is no evolution of chlorine gas. CuO → 2HCl + CuCl2 + H2O Filterate is blueish colour.
(x) Dil. HCl is prepared by dissolving HCl gas in water. It ionises to H3O+ and CT ions. HCl gas is prepared by explosive mixture of equal volumes of hydrogen gas and chlorine gas.
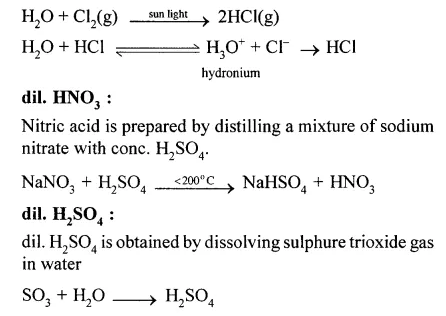
Question 3.
Identify the cation (positive ion) and anion (negative ion) in the following substances, A, B and C. Also identify P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W.
(a) Substance ‘A’is water soluble and gives a curdy white precipitate ‘P’ with silver nitrate solution. ‘P’ is soluble in ammonium hydroxide but insoluble in dil. HNO3. Substance ‘A’ reacts with ammonium hydroxide solution to give a white precipitate ‘Q’ soluble in excess of NH4OH.
(b) A solution of substance ‘B’ is added to barium chloride solution. A white ppt. ‘R’ is formed, insoluble in dil. HCl or HNO3. A dirty green ppt. ‘S’ is formed on addition of ammonium hydroxide to a solution of ‘B’ and the precipitate is insoluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
(c) Substance ‘C’ is a coloured, crystalline salt which on heating decomposes leaving a black residue ‘T’. On addition of copper turnings and cone. H2SO2 to ‘C’ a coloured acidic gas ‘U’ is evolved on heating. A solution of ‘C’ is added to NaOH soln. until in excess. A pale blue ppt. ‘P’ is obtained insoluble in excess of NaOH. A solution of ‘C’ then added to NH4 soln. in excess to gives an inky blue solution ‘V’. A solution of ‘C’ is warmed and hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through it. A black ppt. ‘W’ appears.
Answer:


–Try Also :–




