Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions Chapter-11 Study of Compound D. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Intext , Exe-8 and Previous Year Questions of Chapter-11 Sulphuric Acid Study of Compound-D ICSE Class-10 . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publishers PVT LTD |
| Subject | Concise Chemistry |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | Dr SP Singh |
| Chapter-11 | Study of Compound D Sulphuric Acid |
| Topics | Solutions of Exe-11 with Intext and Previous Year Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions Chapter-11
(Study of Compound-D)
–: Select Topics :–
Intext ,
How to solve Sulphuric Acid Chemistry for ICSE Class 10
Read the Chapter -11 Sulphuric Acid carefully. Focus on reaction involve in Chemical Properties of Sulphuric Acid. Various Step involve with reaction in Purification of Sulphuric Acid . Lab Preparation of Sulphuric Acid .Solve 10 Years Question given related Sulphuric Acid given last of exercise.
Intext , Chapter-11 Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10
(Selina Concise Chemistry Solutions Study of Compound D)
Page-175
Question 1
Comment, sulphuric acid is referred to as
(a) King of chemicals
(b) Oil of vitriol
Answer 1
(a) Sulphuric acid is called King of Chemicals because there is no other manufactured compound which is used by such a large number of key industries.
(b) Sulphuric acid is referred to as Oil of vitriol as it was obtained as an oily viscous liquid by heating crystals of green vitriol.
Question 2
Sulphuric acid is manufactured by contact process
(a) Give two balanced equations to obtain SO2 in this process.
(b) Give the conditions for the oxidation of SO2
(c) Name the catalyst used.
(d) Why H2SO4 is not obtained by directly reacting SO3 with water.
(e) Name the chemical used to dissolve SO3 and also name the product formed.
(f) Name a gas that can be oxidized to sulphur.
Answer 2
(a) Two balanced equations to obtain SO2 is:
(i) 4FeS2 + 11O2 2Fe2O3 +8SO2
(ii) S +O2 SO2
(b) The conditions for the oxidation of SO2 are:
(i) The temperature should be as low as possible. The yield has been found to be maximum at about 4100C-450oC
(ii) High pressure (2 atm) is favoured because the product formed has less volume than reactant.
(iii) Excess of oxygen increases the production of sulphur trioxide.
(iv) Vanadium pentoxide or platinised asbestos is used as catalyst.
(c) Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5)
(d) Sulphuric acid is not obtained directly by reacting SO3 with water because the reaction is highly exothermic which produce the fine misty droplets of sulphuric acid that is not directly absorbed by water.
(e)The chemical used to dissolve SO3 is concentrated sulphuric acid. The product formed is oleum.
(f) Hydrogen sulphide.
Question 3
Why the impurity of arsenic oxide must be removed before passing the mixture of SO2 and air through the catalytic chamber?
Answer 3
Impurity of ARSENIC poisons the catalyst [i.e. deactivates the catalyst]. So, it must be removed before passing the mixture of SO2 air through the catalytic chamber.
Question 4
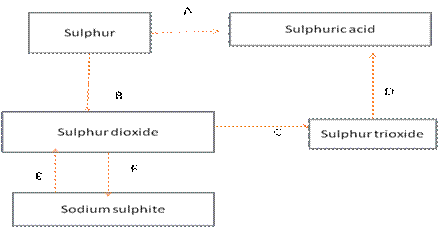
(a) Name the catalyst which helps in the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide in step C.
(b) In the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid, sulphur trioxide is not converted to sulphuric acid by reacting it with water. Instead a two -steps procedure is used. Write the equations for the two steps involved in D.
(c) What type of substance will liberate sulphur dioxide from sodium sulphite in step E?
(d) Write the equation for the reaction by which sulphur dioxide is converted to sodium sulphite in step F.
Answer 4
(a) The catalyst which helps in the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide in step C is Vanadium pentoxide.
(b) The two steps for the conversion of sulphur trioxide to sulphuric acid is:
(i) SO3 + H2SO4H2S2O7
(ii) H2S2O7 + H2O 2H2SO4
(c)The substance that will liberate sulphur dioxide in step E is dilute H2SO4.
(d) The equation for the reaction by which sulphur dioxide is converted to sodium sulphite in step F is:
SO2+2NaOHNa2SO3+H2O
Or
Na2O+SO2Na2SO3
Exercise-11 , Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10
(Concise Chemistry Selina Publishers Solutions )
Page-179
Question 1
Why is water not added to concentrated H2SO4 in order to dilute it?
Answer 1
Water is not added to concentrated acid since it is an exothermic reaction. If water is added to the acid, there is a sudden increase in temperature and the acid being in bulk tends to spurt out with serious consequences.
Question 2
Give two balanced reactions of each type to show the following properties of sulphuric acid.
(a) Acidic nature
(b) Oxidising agent
(c) dehydrating Nature
(d) Non-volatile nature
Answer 2
Balanced reactions are:
(a) Acidic nature:
(i) Dilute H2SO4 reacts with basic oxides to form sulphate and water.
2 NaOH+H2SO4 Na2SO4+2H2O
(ii) CuO+H2SO4 CuSO4+H2O
(iii) It reacts with carbonate to produce CO2.
Na2CO3+H2SO4Na2SO4+H2O+CO2
(b) Oxidising agent:
H2SO4 H2O +SO2 +[O]
Nascent oxygen oxidizes non-metals, metals and inorganic compounds.
For example,
Carbon to carbon dioxide
C+H2SO4 CO2 +H2O +2SO2
Sulphur to sulphur dioxide
S +H2SO4 3SO2 +2H2O
(c) dehydrating Nature
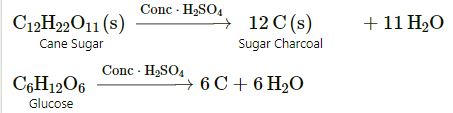
(d) Non-volatile nature:
It has a high boiling point (356oC) so it is considered to be non-volatile. Therefore, it is used for preparing volatile acids like hydrochloric acid, nitric acid from their salts by double decomposition reaction.
NaCl + H2SO4NaHSO4 +HCl
KCl + H2SO4 KHSO4 +HCl
Question 3
Give a chemical test to distinguish between:
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid and dilute hydrochloric acid
(b) Dilute sulphuric acid and conc. sulphuric acid
Answer 3
(a)Bring a glass rod dipped in Ammonia solution near the mouth of each test tubes containing dil. Hel and dil. H2SO4each.
| Dil HCl | Dil. H2SO4 |
| White fumes of ammonium chloride | No such fumes |
(b)
1. Dilute sulphuric acid treated with zinc gives Hydrogen gas which bums with pop sound.
Concentrated H2SO4 gives SO2 gas with zinc and the gas turns Acidified potassium dichromate paper green.
2.Barium chloride solution gives white ppt. with dilute H2SO4, This white ppt. is insoluble in all acids.
Concentrated H2SO4 and NaCl mixture when heated gives dense white fumes if glass rod dipped in Ammonia solution is brought near it.
Question 4
Write balance equation when hot and concentrated sulphuric acid reacts with the following:
(a) Sulphur
(b) NaOH
(c) Sugar
(d) Carbon
(e) Copper
Answer 4
(a) When sulphuric acid reacts with sulphur the product formed is Sulphur dioxide is formed.
S +2H2SO4![]() 3SO2 + 2H2O
3SO2 + 2H2O
(b) When sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide it neutralizes base to form sodium sulphate.
2NaOH + H2SO4 ![]() Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) When sulphuric acid reacts with sugar it forms carbon
C12 H22O11 ![]() 12C + 11H2O
12C + 11H2O
(d) When sulphuric acid reacts with carbon it forms carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide gas.
C +2H2SO4 ![]() CO2 + 2H2O + 2SO2
CO2 + 2H2O + 2SO2 ![]()
(e) When sulphuric acid reacts with copper it forms copper sulphate and sulphur dioxide.
Cu + H2SO4 ![]() CuSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
CuSO4 + 2H2O + SO2 ![]()
Question 5
Why is:
(a) Concentrated sulphuric acid kept in air tight bottles?
(b) H2SO4 is not a drying agent for H2S?
(c) Sulphuric acid used in the preparation of HCl and HNO3? Give equation in both cases.
Answer 5
(a) Concentrated sulphuric acid is hydroscopic substance that absorbs moisture when exposed to air. Hence, it is stored in air tight bottles.
(b) Sulphuric acid is not a drying agent for H2S because it reacts with H2S to form sulphur.
H2SO4+H2S ![]() 2H2O+SO2+S
2H2O+SO2+S ![]()
(c) Concentrated sulphuric acid has high boiling point (356oC). So, it is considered to be non-volatile. Hence, it is used for preparing volatile acids like Hydrochloric acid and Nitric acids from their salts by double decomposition.
NaCl+H2SO4 ![]() NaHSO4 +HCl
NaHSO4 +HCl
NaNO3 +H2SO4 ![]() NaHSO4 +HNO3
NaHSO4 +HNO3
Question 6
What property of conc. H2SO4 is made use of in each of the following cases? Give an equation for the reaction in each case
(a) In the production of HCl gas when it reacts with a chlorine
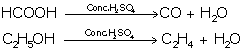
(b) In the preparation of CO from HCOOH
(c) As a source of hydrogen by diluting it and adding a strip of magnesium
(d) In the preparation of sulphur dioxide by warming a mixture of conc. Sulphuric acid and copper -turnings.
(e) Hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through concentrated sulphuric acid
(f) Its reaction with (i) ethanol (ii) carbon
Answer 6
(a) Due to its reducing property. i.e, it is a non-volatile acid.
NaCl+ H2SO4 ![]() NaHSO4 + HCl
NaHSO4 + HCl
(Conc.)
(b) It is a dehydrating agent.
HCOOH ![]() CO + H2O
CO + H2O
(c) Magnesium is present above hydrogen in the reactivity series so sulphuric acid is able to liberate hydrogen gas by reacting with magnesium strip.
Mg + H2SO4 ![]() MgSO4+H2
MgSO4+H2
(d) Due to its oxidizing character
Cu +H2SO4 ![]() CuSO4 +2H2O +SO2
CuSO4 +2H2O +SO2
(e) Due to its oxidizing property Hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through concentrated sulphuric acid to liberate sulphur dioxide and sulphur is formed.
H2S + H2SO4 ![]() S + 2H2O + SO2
S + 2H2O + SO2
(f)
(i) Ethanol
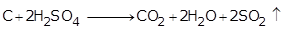
(ii) Carbon
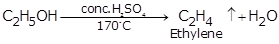
Question 7
What is the name given to the salts of:
(a) Sulphurous acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
Answer 7
The name of the salt of
(a) Hydrogen sulphites and Sulphites.
(b) Sulphate and bisulphate.
Question 8
Give reasons for the following.
(a) Sulphuric acid forms two types of salts with NaOH
(b) A piece of wood becomes black when concentrated sulphuric acid is poured on it
(c) Brisk effervescence is seen when oil of vitriol is added to sodium carbonate.
Answer 8
(a) Two types of salts are formed when sulphuric acid reacts with NaOH because sulphuric acid is dibasic.
NaOH + H2SO4 ![]() NaHSO4 + H2O
NaHSO4 + H2O
2NaOH + H2SO ![]() 4Na2SO4 + 2H2O
4Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(b) A piece of wood becomes black when concentrated sulphuric acid is poured on it because it gives a mass of carbon.
(c) When sulphuric acid is added to sodium carbonate it liberates carbon dioxide which produces brisk effervescence.
Na2CO3+H2SO4 ![]() Na2SO4 +H2O+CO2
Na2SO4 +H2O+CO2 ![]()
Question 9
Copy and complete the following table:
| Column 1
Substance reacted with acid |
Column 2
Dilute or concentrated acid |
Column 3
Gas |
| Hydrogen | ||
| Carbon dioxide | ||
| Only chlorine |
Answer 9
| Column 1
Substance reacted with acid |
Column 2
Dilute or concentrated acid |
Column 3
Gas |
| Substance reacted with acid | Dilute or concentrated sulphuric acid | Gas |
| Zinc | Dilute sulphuric acid | Hydrogen |
| Calcium carbonate | Concentrated sulphuric acid | Carbon dioxide |
| Bleaching power CaOCl2 | Dilute sulphuric acid | only chlorine
|
Page-180
Question 10
The following are the typical properties of dilute acid. complete them by inserting suitable words :
(i) Active metal + acid → …………. + ……………
(ii) Base + Acid → ………….. + …………….
(iii) Carbonate/hydrogen carbonate + Acid → …………. + …………. + …………..
(iv) Sulphite/hydrogen sulphite + Acid → …………. + ………… + ………….
(v) Sulphide + Acid → ……………. + ………………..
Answer 10
(i) Active metal + acid → Metal sulphate + Hydrogen
(ii) Base + Acid → salt + water
(iii) Carbonate/hydrogen carbonate + Acid → Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
(iv) Sulphite/hydrogen sulphite + Acid → Salt + Water + Sulphur dioxide
(v) Sulphide + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen sulphide
Question 11
(a) Which property of sulphuric acid accounts for its use as a dehydrating agent?
(b) Concentrated sulphuric acid is both an oxidizing agent and a non-volatile acid. Write one equation. Each to illustrate the above mentioned properties of sulphuric acid.
Answer 11
(a) Sulphuric acid is powerful dehydrating agent on account of its strong affinity towards water.
(b) Concentrated sulphuric acid as
Oxidising agent:
The oxidising property of conc. sulphuric acid its due to the fact that on thermal decomposition, it yields nacent oxygen [O].
H2SO4→ H2O + SO2 + [O]
Non-volatile acid:
conc. sulphuric acid has high boiling point (338°C) that why it is said to be a non volatile compound, therefore it is used for preparing volatile acids like hydrochloric acids, nitric acids from there salts by double decomposition
H2SO4 + NaCl → NaHSO4 + HCl
Question 12
Some properties of sulphuric acid are listed below. Choose the property A, B, C or D which is responsible for the reactions (i) to (v). Some properties may be repeated:
A. Typical Acid
B. Dehydrating agent
C. Non-volatile acid
D Oxidising agent
(i) C12H22O11 +nH2SO4 ![]() 12C + 11H2O + nH2SO4
12C + 11H2O + nH2SO4
(ii) S + 2H2SO4 ![]() 3SO2 +2H2O
3SO2 +2H2O
(iii) NaCl +H2SO4 ![]() NaHSO4 + HCl
NaHSO4 + HCl
(iv) CuO + H2SO4 ![]() CuSO4 +H2O
CuSO4 +H2O
(v) Na2CO3 + H2SO4 ![]() Na2SO4 + H2O +CO2
Na2SO4 + H2O +CO2
Answer 12
(i) B
(ii) D
(iii) C
(iv) A
(v) A
Question 13
(a) Name the acid formed when sulphur dioxide dissolves in water.
(b) Name the gas released when sodium carbonate is added to a solution of sulphur dioxide.
Answer 13
(a) The acid formed when sulphur dioxide dissolves in water is sulphurous acid.
(b) Carbon dioxide gas is released when sodium carbonate is added to solution of sulphur dioxide.
Chapter-11 , Sulphuric Acid Selina Solution (Previous Year Question)
Page-180
Question 2008
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid will produce a white precipitate when added to a solution of :
(i) Copper nitrate
(ii) Zinc nitrate
(iii) Lead nitrate
(iv) Sodium nitrate
Identify the following substance: Liquid E can be dehydrated to produce ethene.
(c) Copy and complete the following table relating to an important industrial process and its final output.
| Name of process | Inputs | Catalyst | Equation for catalyzed reaction output |
| Contact process | Sulphur dioxide + oxygen |
Making use only of substances given : dil. sulphuric acid, sodium carbonate, zinc, sodium. sulphite, lead, calcium carbonate : Give equations for the reactions by which you could obtain :
(i) hydrogen
(ii) sulphur dioxide
(iii). carbon dioxide
(iv)zinc carbonate [2 steps]
What property of conc. H2SO4 :
(i) is used in the action when sugar turns black in its presence.
(ii) allows it to be used in the preparation of HCl and HNO3 acids.
(iii) Write the equations for :
(iv) dil. H2SO4 and barium chloride
(v) dil. H2SO4 and sodium sulphide
Answer 2008
(a) (C) Lead nitrate
(b) Liquid E is Ethanol.
(c)
| Name of process | Inputs | Catalyst | Equation for catalyzed reaction output | output |
| Contact process | Sulphur dioxide + oxygen | Platinum or V2O5 | 2SO2 + O2 ⇄ 2SO3 | Sulphuric acid |
(d)
(i) Zn + dil. H2SO4→ ZnSO4 + H2
(ii) Na2CO3 + dil. H2SO4→ Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2
(iii) Pb(NO3) + dil. H2SO4→ PbSO4 + 2HNO3
(iv) Zn + dil. H2SO4→ ZnSO4 + H2
ZnSO4 + Na2CO3→ ZnCO3 + Na2SO4
(e)
(i) The property of concentrated sulphuric acid which allows it to be used in is used in the action when sugar turns black in its presence is its dehydrating property.
(ii) The property of concentrated sulphuric acid which allows it to be used in the preparation of hydrogen chloride and nitric acid is its non-volatility.
H2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question 2009
(a) Name the gas evolved [formula is not acceptable]. The gas that can be oxidised to sulphur.
Answer 2009
Hydrogen Chloride
Question 2010
(a) Give the equation for :
(i) Heat on sulphur with conc. sulphuric acid
(ii) Reaction of – sugar with conc. sulphuric acid.
(b) Give a balanced equation for the conversion of zinc oxide to zinc sulphate.
(c) Select the correct answer from A, B, C.
A. Sodium hydroxide solution
B A weak acid
C Dilute sulphuric acid.
The solution which liberates sulphur dioxide gas, from sodium sulphite.
Answer 2010
(a)
(i) S + H2SO4 → 3SO2 +2H2O.
(ii) C12H22O11 + Conc. H2SO4 → 6C + 6H2O
(b) ZnO+ H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2O.
(c) C) Dilute sulphuric acid.
Question 2011
(a) State your observation when – Sugar crystals are added to a hard glass test tube containing conc. sulphuric acid.
(b) Choose the correct answer from the choices – The gas evolved when dil. sulphuric acid reacts with iron sulphide.
(i) Hydrogen sulphide
(ii) Sulphur dioxide
(iii) Sulphur trioxide
(iv) Vapour of sulphuric acid
(c) Give a balanced equation for :
(i) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured over sodium sulphite.
(ii) Manufacture of sulphuric acid by the – contact process.
(d) State the property of sulphuric acid shown by the reaction of conc. sulphuric acid when heated with
(i) potassium nitrate
(ii) carbons
Answer 2011 ( Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 )
(a) Charring of sugar takes place. Sulphuric acid dehydrates sugar leaving behind carbon which is black in colour.
(b) i. Hydrogen sulphide
(c)
i.![]()
ii.
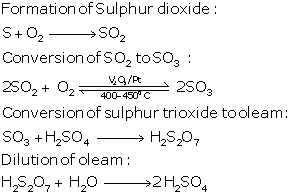
(d)
(i) Non-volatile nature
(ii) as an oxidising agent
Page-181
Question 2012
(a) Name – The gas produced on reaction of dilute sulphuric acid with a metallic sulphide.
(b) Some properties of sulphuric acid are listed below. Choose the role played by sulphuric acid as A, B, C or D which is responsible for the reactions (i) to (v). Some role/s may be repeated.
- Dilute acid
2 Dehydrating agent
- 3.Non-volatile acid
- 4.Oxidising agent
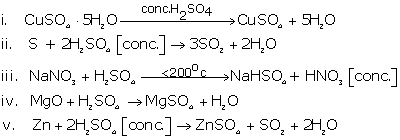
(c) Give balanced equation for the reaction : Zinc sulphide and dilute sulphuric acid. (2019)
Answer 2012 ( Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 )
(a) Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S).
(b)
(i) (B) Dehydrating agent
(ii) (D) Oxidising agent
(iii). (C) Non-volatile acid
(iv) (A) Dilute acid
(v) (D) Oxidising agent
(c) ZnS+ dil.H2SO4→ ZnSO4 + H2S
Question 2013
(a) State one appropriate observation for : Conc. H2SO4 is added to a crystal of hydrated copper sulphate. (2016)
(b) In the given equation – S + 2H2SO4→3SO2 + 2H2O :
Identify the role played by conc. H2SO4.
(i) Non-volatile acid
(ii) Oxidising agent
(iii). Dehydrating agent
(iv) None of the above
(c) Give a balanced equation for : Dehydration of concentrated sulphuric acid with sugar crystals.
(d) Identify the substance underlined : A dilute mineral acid which forms a white precipitate when treated with barium chloride solution.
Answer 2013
(a) when Conc. H2SO4 is added to a crystal of hydrated copper sulphate, it removes water of crystallization from salt.
(b)
Option ii. Oxidising agent
(c) C12H22O11+ Conc. H2SO4 → 6C + 6H2O
(d) Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
Question 2014 ( Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 )
(a) Write balanced equations for the following : Action of concentrated sulphuric acid on carbon.
(b) Distinguish between the following pairs of compounds using the test given within brackets. Dilute sulphuric acid and dilute hydrochloric acid [using barium chloride solution].
(c) State the conditions required for the following reactions to take place : The conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide.
(d) Give one equation each to show the following properties of sulphuric acid :
(i) Dehydrating property
(ii) Acidic nature
(iii). As a non-volatile acids
Answer 2014
(a) C + H2SO4→ CO2 + 2H2O + 2SO2.
(b) Sulphuric acid precipitates the insoluble sulphate of barium from the solution of barium chloride.
BaCl2 + H2SO4→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
Dilute HCl does not react with barium chloride solution, and thus, no precipitate is produced in the reaction.
(c) Two conditions for the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide is as follows:
Temperature: 450-500° C Catalyst: V2O5
![]()
(d)
(i) Dehydrating property of sulphuric acid:
H2SO4 has a great affinity for water, and therefore, it acts as a dehydrating agent.
(ii)Acidic nature of sulphuric acid:
It acts as a strong dibasic acid.
H2SO4→ 2Hi+ + SO42-
It reacts with metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides, carbonates etc. to form metallic sulphates and hydrogen at ordinary temperature.
Mg + H2SO4→ MgSO4 + H2↑
CuO + H2SO4→ CuSO4 + H2O
2NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
ZnCO3 + H2SO4→ ZnSO4 + H2O + CO2↑
(iii). As a non-volatile acid:
It has a high boiling point, so it is used to prepare volatile acids such as HCl, HNO3 and acetic acid from their salts.
NaCl + H2SO4→ NaHSO4 + HCl
NaNO3 + H2SO4→ NaHSO4 + HNO3
CH3COONa + H2SO4→ NaHSO4 + CH3COOH
Question 2015 ( Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 )
(a) In the manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process, give the equations for the conversion of sulphur trioxide to sulphuric acid.
(b) Give equations for the action of sulphuric acid on
(i) Potassium hydrogen carbonate
(ii) Sulphur
(c) Identify the acid in each case.
(i) Acid which produces sugar charcoal from sugar
(ii) Acid on mixing with lead nitrate solution produces white ppt. which is insoluble even on heating
Answer 2015
(a) In the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid, the equations for the conversion of sulphur trioxide to sulphuric acid are
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
(oleum or pyro sulphuric acid)
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
(b)
(i) Action of sulphuric acid on potassium hydrogen carbonate
2KHCO3+ H2SO4→ K2SO4+ 2H2O + 2CO2↑
(ii) Action of sulphuric acid on sulphur
S + 2H2SO4→ 3SO2 + 2H2O
(c)
(i) Concentrated sulphuric acid
(ii) Concentrated sulphuric acid
-: End of Sulphuric Acid ICSE Class-10 :-
Return to:- Concise Selina Solutions for ICSE Chemistry Class-10
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends


2015 c ii) is wrong