Ecosystem MCQs Type Questions with Answer for ISC Class 12 Biology. These MCQs / Objective Type Questions is based on latest reduced syllabus according 2021-22 session on bifurcated pattern. Main motto of MCQ Type Question is cracking the next upcoming Sem-2 exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ISC Class-12 Biology.
ISC Class 12 Biology Ecosystem MCQs Type Questions with Answer
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12th (XII) |
| Subject | Biology |
| Chapter | Ecosystem |
| Syllabus | on bifurcated syllabus (after reduction) |
| Session | 2021-22 |
| Bifurcated | Sem-2 |
| Topic | MCQs / Objective Type Question |
ISC Ecosystem MCQs Questions with Answers for Class-12 Biology
Question 1: In ecological succession from pioneer to climax community, the biomass shall
(a) decrease
(b) increase and then decrease
(c) no relation between these communities
(d) increase continuously
Answer : (d) increase continuously
Question 2: Submerged Rooted Hydrophyte are:
(a) Uticularia
(b) Prapa
(c) Nymphea
(d) Vallisnaria
Answer : (d) Vallisnaria
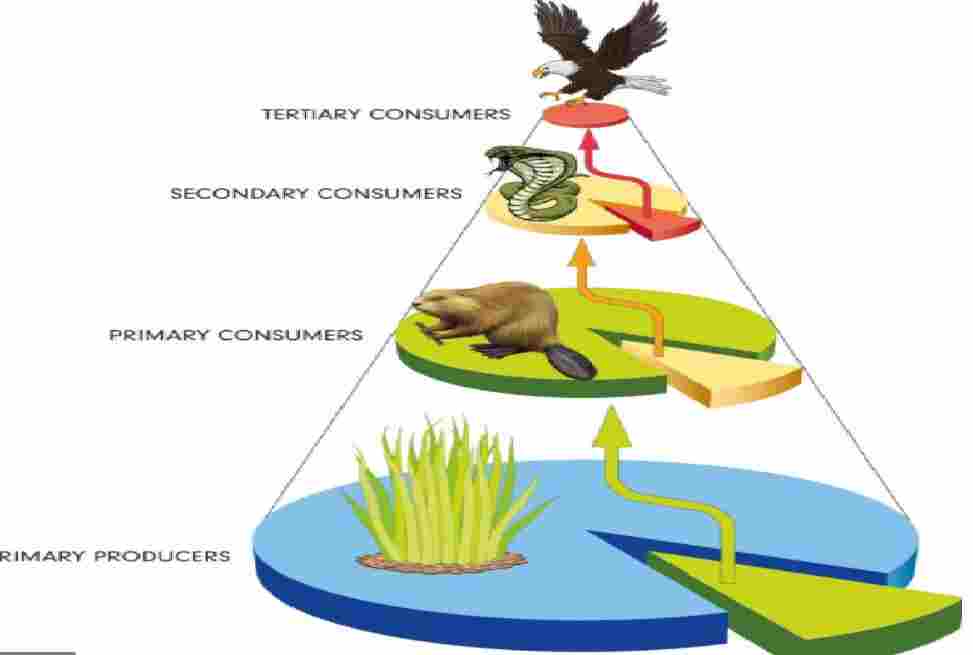
Question 3: Which one is the correct food chain ?
(a) Eagle → Snake → Grasshopper → Grass → Frog
(b) Frog → Snake → Eagle → Grasshopper → Grass
(c) Grasshopper → Grass → Snake ® Frog → Eagle
(d) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog ® Snake → Eagle
Answer : (d) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog ® Snake → Eagle
Question 4: Which one of the following is not an abiotic component?
(a) Temperature
(b) Decomposers
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Answer : (b) Decomposers
Question 5: Energy flow in ecosystem is
(a) Unidirectional
(b) Multidirectional
(c) Bidirectional
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) Unidirectional
Question 6: In an ecosystem abiotic components includes which of the following ?
(a) Flow of energy
(b) Cycling of materials
(c) Consumers
(d) Flow of energy and cycling of materials
Answer : (d) Flow of energy and cycling of materials
Question 7: Which one of the following is one of the characteristics of a biological community?
(a) Stratification
(b) Natality
(c) Mortality
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) Stratification
Question 8: During the process of ecological succession the changes that take place in communities are
(a) Orderly and sequential
(b) Random
(c) Very quick
(d) Not influenced by the physical environment
Answer : (a) Orderly and sequential
Question 9: Given below is one of the types of ecological pyramids. This type represents
(a) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland
(b) Pyramid of biomass in a follow land
(c) Pyramid of biomass in a lake
(d) Energy pyramid in a spring
Answer : (c) Pyramid of biomass in a lake
Question 10: Climax community is in a state of
(a) equilibrium
(b) disorder
(c) constant change
(d) non-equilibrium
Answer : (a) equilibrium
Question 11: Which of the following type of ecosystem is expected in an area where evaporation exceeds precipitation, and mean annual rainfall is below 100mm
(a) Desert
(b) Mangrove
(c) Grassland
(d) Shrubby forest
Answer : (a) Desert
Question 12: The zone at the edge of a lake or ocean which is alternatively exposed to air and immersed in water is called
(a) Littoral zone
(b) Lentic one
(c) Benthic zone
(d) Pelagic zone
Answer : (a) Littoral zone
Question 13: Soil particle determine the character of:
(a) Organisation
(b) Biomass
(c) Area capacity
(d) Soil plants
Answer : (a) Organisation
Question 14: Edaphic factor refers to
(a) Soil
(b) Relative humidity
(c) Altitude
(d) Water
Answer : (a) Soil
Question 15: Plant roots soil water is:
(a) Cellular water
(b) Surface water
(c) Humidity water
(d) Gravitational water
Answer : (d) Gravitational water
Question 16: The term “detritivore” includes
(a) decomposers
(b) primary consumers
(c) secondary consumers
(d) autotrophs
Answer : (a) decomposers
Question 17: The earth is an open system with respect to
(a) organisms
(b) chemicals
(c) energy
(d) all of the above
Answer : (c) energy
Question 18: Both hydrach and xerarch successions:
(a) Take same time
(b) Have similar sere
(c) Lead to mesic conditions
(d) Have same pioneer species
Answer : (c) Lead to mesic conditions
Question 19: An ecosystem is a
(a) group of components that interact with one another.
(b) group of interacting species in one place at one time.
(c) biological community and component of the physical environment with which the community interacts.
(d) group of interacting chemicals and their cycles.
Answer : (c) biological community and component of the physical environment with which the community interacts.
Question 20: Which of the following is/are example(s) of man-made ecosystem?
(a) Herbarium
(b) Crop fields
(c) Aquarium
(d) Both b) and c)
Answer : (d) Both b) and c)
Question 21: An ecosystem is a
(a) group of components that interact with one another
(b) group of interacting species in one place at one time
(c) biological community and component of the physical environment with which the community interacts
(d) group of interacting chemicals and their cycles
Answer : (c) biological community and component of the physical environment with which the community interacts
Question 22: Identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of an ecosystem gives its
(a) productivity
(b) stratification
(c) species composition
(d) all of these
Answer : (c) species composition
Question 23: Two main structural features of an ecosystem are
(a) species composition and stratification
(b) species composition and productivity
(c) productivity and energy flow
(d) nutrient cycling and stratification
Answer : (a) species composition and stratification
Question 24: Primary productivity
(a) is equal to the standing crop of an ecosystem.
(b) is greatest in freshwater ecosystems.
(c) is the rate of conversion of light to chemical energy in an ecosystem
(d) is inverted in some aquatic ecosystems
Answer : (c) is the rate of conversion of light to chemical energy in an ecosystem
Question 25: An inverted pyramid of biomass can be found in which ecosystem?
(a) Marine
(b) Forest
(c) Grass land
(d) Tundra
Answer : (a) Marine
Question 26: Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called
(a) enumeration
(b) stratification
(c) species composition
(d) none of these
Answer : (b) stratification
Question 27: Secondary Succession takes place on/in
(a) Degraded forest
(b) Bare rock
(c) Newly cooled lava
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) Degraded forest
Question 28: Two main structural features of an ecosystem are
(a) species composition and stratification
(b) species composition and productivity
(c) productivity and energy flow
(d) nutrient cycling and stratification
Answer : (a) species composition and stratification
Question 29: Which of the following is an example of man-made ecosystem?
(a) Aquarium
(b) Herbarium
(c) Tissue culture
(d) All of these
Answer : (a) Aquarium
Question 30: Identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of an ecosystem gives its
(a) productivity
(b) stratification
(c) species composition
(d) all of these
Answer : (c) species composition
Question 31: Primary productivity
(a) is equal to the standing crop of an ecosystem.
(b) is greatest in freshwater ecosystems.
(c) is the rate of conversion of light to chemical energy in an ecosystem.
(d) is inverted in some aquatic ecosystems
Answer : (c) is the rate of conversion of light to chemical energy in an ecosystem.
Question 32: How much of the net primary productivity of a terrestrial ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores?
(a) 10%
(b) 1%
(c) 40%
(d) 90%
Answer : (a) 10%
Question 33: Maximum absorption of rainfall water is done by
(a) Tropical deciduous forest
(b) Tropical evergreen forest
(c) Tropical savannah
(d) Scrule forest
Answer : (b) Tropical evergreen forest
Question 34: Which of the following is called as a detrivore?
(a) An animal feeding on decaying organic matter
(b) An animal feeding on a plant
(c) A plant feeding on an animal
(d) An animal feeding on another animal
Answer : (a) An animal feeding on decaying organic matter
Question 35: At the trophic level of consumers, the rate at which food energy is assimilated, is called:
(a) Secondary productivity
(b) Gross primary productivity
(c) Net primary productivity
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) Secondary productivity
Question 36: Energy transferred from one trophic level to another
(a) 5%
(b) 10%
(c) 15%
(d) 20%
Answer : (b) 10%
Question 37: If the carbon atoms fixed by producers already have passed through three species, the trophic level of the last species would be
(a) tertiary consumer
(b) secondary consumer
(c) tertiary producer
(d) scavenger
Answer : (a) tertiary consumer
Question 38: Best soil for plant growth is:
(a) Grit
(b) Sandy
(c) Soily
(d) Clay
Answer : (d) Clay
Question 39: The process of mineralisation by micro organisms helps in the release of:
(a) inorganic nutrients from humus
(b) both organic and inorganic nutrients from detritus
(c) organic nutrients from humus
(d) inorganic nutrients from detritus and formation of humus.
Answer : (a) inorganic nutrients from humus
Question 40: Productivity is the rate of production of biomass expressed in terms of:
(i) (kcal m-1) yr-1
(ii) g-2yr-1
(iii) g-1 yr-1
(iv) (kcal m-2 yr-1
(a) ii
(b) iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) i and iii.
Answer : (c) ii and iv
Question 41: Which of the following is not a producer?
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Agaricus
(c) Volvox
(d) Nostoc.
Answer : (b) Agaricus
Question 42: Which of the following ecosystems is most productive in terms of net primary production?
(a) Deserts
(b) Tropical rainforests
(c) Oceans
(d) Estuaries.
Answer : (b) Tropical rainforests
Question 43: The rate at which light energy is converted into chemical energy of organic molecules is the ecosystem’s
(a) net primary productivity
(b) gross secondary productivity
(c) net secondary productivity
(d) gross primary productivity
Answer : (d) gross primary productivity
Question 44: The sequence of communities of primary succession in water is
(a) phytoplankton, rooted submerged hydrophytes, floating hydrophytes, reed swamp, sedges, meadow and trees
(b) free-floating hydrophytes, sedges, phytoplankton, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees
(c) phytoplankton, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses and trees.
(d) phytoplankton, sedges, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees.
Answer : (a) phytoplankton, rooted submerged hydrophytes, floating hydrophytes, reed swamp, sedges, meadow and trees
Question 45: The major reservoir for phosphorous is
(a) Aquifers
(b) Soil and rocks
(c) The atmosphere
(d) Clouds
Answer : (b) Soil and rocks
Question 46: The reservoir for the gaseous type of bio-geo chemical cycle exists in
(a) atmosphere
(b) stratosphere
(c) ionosphere
(d) lithosphere
Answer : (a) atmosphere
Question 47: If the carbon atoms fixed by producers already have passed through three species, the trophic level of the last species would be
(a) tertiary consumer
(b) secondary consumer
(c) tertiary producer
(d) scavenger
Answer : (a) tertiary consumer
Question 48: What is the annual net primary productivity of whole biosphere?
(a) 170 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter.
(b) 165 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter.
(c) 160 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter.
(d) 155 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter.
Answer : (a) 170 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter.
Question 49: Which of the following pyramids can never be inverted in a natural ecosystem?
(a) pyramid of numbers
(b) pyramid of energy
(c) pyramid of biomass
(d) all can be inverted
Answer : (b) pyramid of energy
Question 50: Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?
(a) Dry weight
(b) Number of individuals
(c) Rate of energy flow
(d) Fresh weight
Answer : (d) Fresh weight
–: End of Ecosystem MCQs for ISC Class-12 Type Questions :–
-: also visit :-
- ISC Sem-2 Question Bank Class-12
- Sem-2 ISC Specimen Paper for Class-12
- ISC Class-12 Textbook Solutions ,Syllabus, Solved Paper
- Previous Year Question Paper for ISC Class-12
Please share with your ISC friends if it is helpful
Thanks