Pythagoras Theorem Class-9th Concise Selina ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter-13. We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-13 Pythagoras Theorem for ICSE Class-9 Concise Selina Mathematics by R K Bansal.
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-13 A and Exe-13 B, to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics .
Pythagoras Theorem Class-9th Concise Selina ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter-13
–: Select Topic :–
Exercise – 13 A, Pythagoras Theorem Class-9th Concise Selina ICSE Maths Solutions
Question 1
A ladder 13 m long rests against a vertical wall. If the foot of the ladder is 5 m from the foot of the wall, find the distance of the other end of the ladder from the ground.
Answer
The pictorial representation of the given problem is given below,

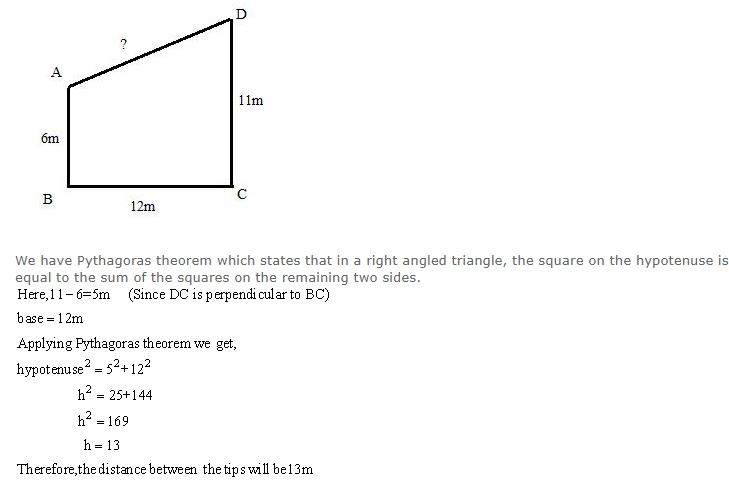
Therefore, the distance of the other end of the ladder from the ground is 12m
Question 2
A man goes 40 m due north and then 50 m due west. Find his distance from the starting point.
Answer
Here , we need to measure the distance AB as shown in the figure below,

Therefore the required distance is 64.03 m.
Question 3
In the figure: PSQ = 90o, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm. Calculate the length of PR.
…………….
Answer
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.

First, we consider the ΔPQS and applying Pythagoras theorem we get,
Question 4
The given figure shows a quadrilateral ABCD in which AD = 13 cm, DC = 12 cm, BC = 3 cm and ABD = BCD = 90o. Calculate the length of AB.
…………………
Answer
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
First, we consider the ΔBCD and applying Pythagoras theorem we get,

The length of AB is 4 cm.
Question 5
AD is drawn perpendicular to base BC of an equilateral triangle ABC. Given BC = 10 cm, find the length of AD, correct to 1 place of decimal.
Answer
Since ABC is an equilateral triangle therefore, all the sides of the triangle are of same measure and the perpendicular AD will divide BC in two equal parts..
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
Here, we consider the and applying Pythagoras theorem we get

Question 6
In triangle ABC, given below, AB = 8 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC= 3 cm. Calculate the length of OC.
Answer
We have Pythagoras theorem which states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
First, we consider the and applying Pythagoras theorem we get,

Question 7
In triangle ABC,
AB = AC = x, BC = 10 cm and the area of the triangle is 60 cm2. Find x.
Answer
Here, the diagram will be,

We have Pythagoras theorem which states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
Since, ABC is an isosceles triangle, therefore perpendicular from vertex will cut the base in two equal

Therefore, x is 13cm
Question 8
If the sides of triangle are in the ratio 1 : : 1, show that is a right-angled triangle.
Answer
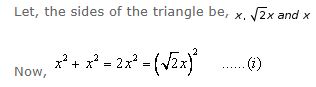
Here, in (i) it is shown that, square of one side of the given triangle is equal to the addition of square of other two sides. This is nothing but Pythagoras theorem which states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
Therefore, the given triangle is a right angled triangle.
Question 9
Two poles of heights 6 m and 11 m stand vertically on a plane ground. If the distance between their feet is 12 m; find the distance between their tips.
Answer
The diagram of the given problem is given below,
Question 10
In the given figure, AB//CD, AB = 7 cm, BD = 25 cm and CD = 17 cm; find the length of side BC.
……………….
Answer
Take M be the point on CD such that AB = DM.
So DM = 7cm and MC = 10 cm
Join points B and M to form the line segment BM.
So BM || AD also BM = AD.

Question 11
In the given figure, ∠B = 90°, XY || BC, AB = 12cm, AY = 8cm and AX: XB = 1: 2 = AY: YC. Find the lengths of AC and BC.
………………
Answer
Given that AX: XB = 1: 2 = AY: YC.
Let x be the common multiple for which this proportion gets satisfied.
So, AX = 1x and XB = 2x
AX + XB = 1x + 2x = 3x
⇒ AB = 3x .….(A – X – B)
⇒ 12 = 3x
⇒ x = 4
AX = 1x = 4 and XB = 2x = 2 × 4 = 8
Similarly,
AY = 1y and YC = 2y
AY = 8…(given)
⇒ 8 = y
∴ YC = 2y = 2 × 8 = 16
∴ AC = AY + YC = 8 + 16 = 24 cm
∆ABC is a right angled triangle. …. Given
∴ By Pythagoras Theorem, we get
⇒ AB2 + BC2 = AC2
⇒ BC2 = AC2 – AB2
⇒ BC2 = (24)2 – (12)2
⇒ BC2 = 576 – 144
⇒ BC2 = 432

Question 12
In ΔABC, …….. Find the sides of the triangle, if:
(i) AB = (x – 3) cm, BC = (x + 4) cm and AC = (x + 6) cm
(ii) AB = x cm, BC = (4x + 4) cm and AC = (4x + 5) cm
Answer


Pythagoras Theorem Class-9th Concise Selina ICSE Maths Solutions Exercise – 13 B
Question 1
In the figure, given below, AD BC. Prove that: c2 = a2 + b2 – 2ax.
………….
Answer
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
First, we consider the ΔACD and applying Pythagoras theorem we get,

Question 2
In equilateral Δ ABC, AD…. BC and BC = x cm. Find, in terms of x, the length of AD.
Answer

Question 3
ABC is a triangle, right-angled at B. M is a point on BC. Prove that:
AM2 + BC2 = AC2 + BM2.
Answer
The pictorial form of the given problem is as follows,

Question 4
M andN are the mid-points of the sides QR and PQ respectively of a PQR, right-angled at Q. Prove that:
(i) PM2 + RN2 = 5 MN2
(ii) 4 PM2 = 4 PQ2 + QR2
(iii) 4 RN2 = PQ2 + 4 QR2
(iv) 4 (PM2 + RN2) = 5 PR2
Answer

We draw , PM,MN,NR
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
Since, M andN are the mid-points of the sides QR and PQ respectively, therefore, PN=NQ,QM=RM



Question 5
In triangle ABC, ∠B = 90o and D is the mid-point of BC. Prove that: AC2 = AD2 + 3CD2.
Answer
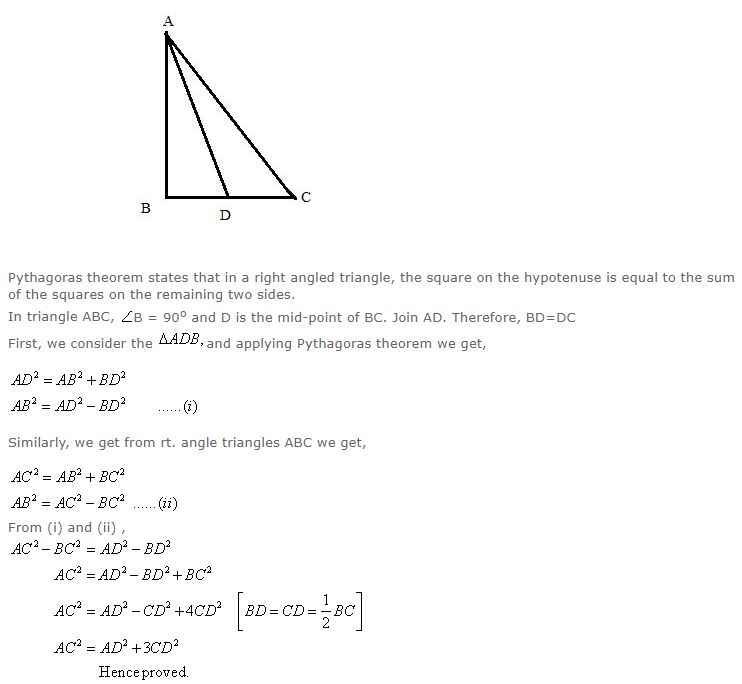
Question 6
In a rectangle ABCD, prove that:
AC2 + BD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2.
Answer

Question 7
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠B = 900 and D = 900. Prove that: 2AC2 – AB2 = BC2 + CD2 + DA2
Answer

Question 8
O is any point inside a rectangle ABCD. Prove that: OB2 + OD2 = OC2 + OA2.
Answer
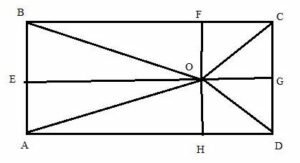
Draw rectangle ABCD with arbitrary point O within it, and then draw lines OA, OB, OC, OD. Then draw lines from point O perpendicular to the sides: OE, OF, OG, OH.
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
Using Pythagorean theorem we have from the above diagram:
OA2 = AH2 + OH2 = AH2 + AE2
OC2 = CG2 + OG2 = EB2 + HD2
OB2 = EO2 + BE2 = AH2 + BE2
OD2 = HD2 + OH2 = HD2 + AE2
Adding these equalities we get:
OA2 + OC2 = AH2 + HD2 + AE2 + EB2
OB2 + OD2 = AH2 + HD2 + AE2 + EB2
From which we prove that for any point within the rectangle there is the relation
OA2 + OC2 = OB2 + OD2
Hence Proved.
Question 9
In the following figure, OP, OQ and OR are drawn perpendiculars to the sides BC, CA and AB respectively of triangle ABC. Prove that:
AR2 + BP2 + CQ2 = AQ2 + CP2 + BR2
……………..
Answer
Here, we first need to join OA, OB, and OC after which the figure becomes as follows,

From (vii) and (viii), we get,
AR2 + BP2 + CQ2 = AQ2 + CP2 + BR2
Hence proved.
Question 10
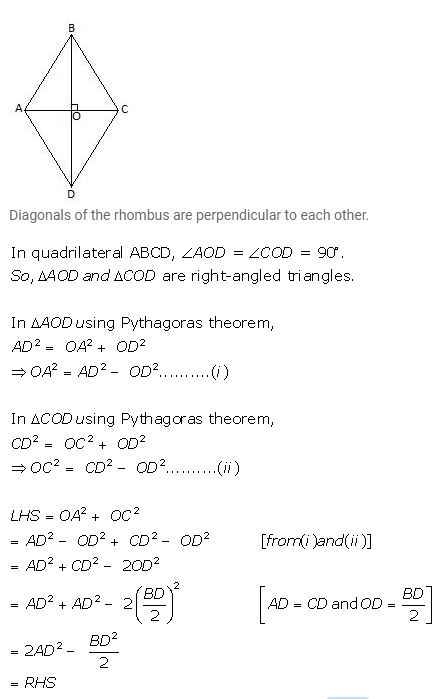
Diagonals of rhombus ABCD intersect each other at point O. Prove that:
OA2 + OC2 = 2AD2 ……….
Answer
Question 11
In the figure AB = BC and AD is perpendicular to CD. Prove that:
AC2 = 2BC. DC.
Answer
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
We consider the ΔACD and applying Pythagoras theorem we get,
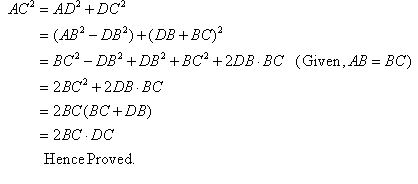
Question 12
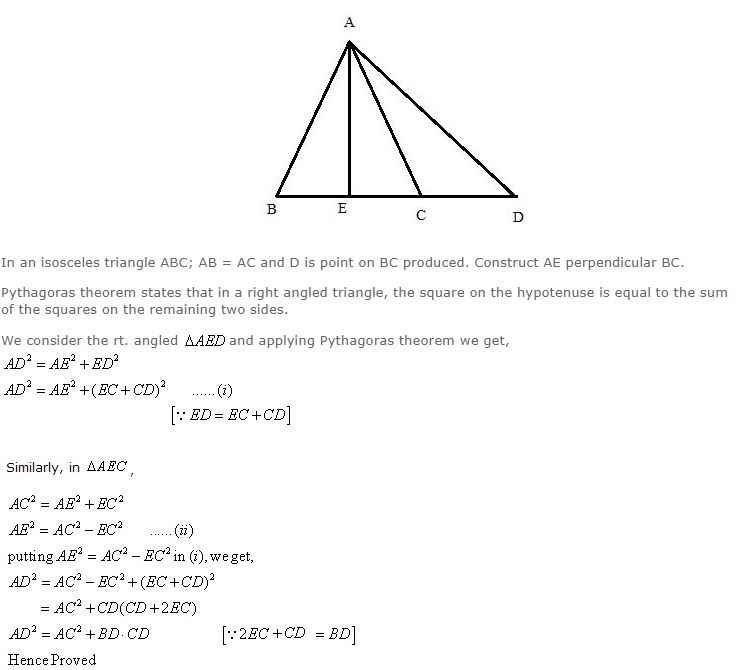
In an isosceles triangle ABC; AB = AC and D is point on BC produced. Prove that:
AD2 = AC2 + BD.CD.
Answer
Question 13
In triangle ABC, angle A = 90o, CA = AB and D is point on AB produced. Prove that DC2 -BD2 = 2AB.AD.
Answer
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
We consider the rt. angled and applying Pythagoras theorem we get,

Question 14
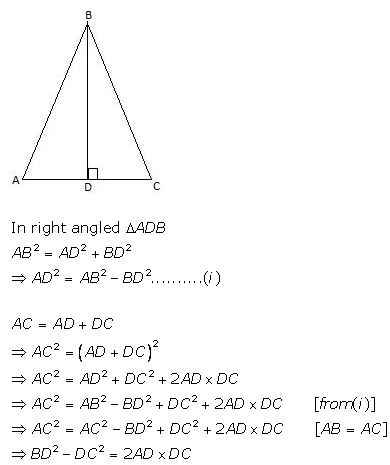
In triangle ABC, AB = AC and BD is perpendicular to AC. Prove that: BD2 – CD2 = 2CD × AD.
Answer
Question 15
In the following figure, AD is perpendicular to BC and D divides BC in the ratio 1: 3.
Prove that : 2AC2 = 2AB2 + BC2
Answer

— End of Pythagoras Theorem Class-9th Concise Selina Solutions :–
Return to – Concise Selina Maths Solutions for ICSE Class -9