Srijan Class-9 Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-8. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check-1, to 2, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type ( including True False), Application / Skill ( Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.

Solutions of Srijan Class-9 Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE Biology Ch-8
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-8 | Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check-1, to 2, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Ch-8 Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 1 (Page 100)
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
1. In fungi, the cell wall is made up of …………………….. and ………………………. .
2. The fungi have ……………………… mode of nutrition.
3. The edible mushroom is ……………….. and inedible mushroom is …………………
4. Tiny filament of Rhizopus that penetrate the substratum are called ……………….
5. The mass of tangled hyphase of a fungus is called ………………..
Answer:
1. Fungal Cellulose and Chitin.
2. Heterotopic.
3. Button.
4. Hyphae.
5. Mycelium
Ch-8 Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 2 (Page 102)
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Irradiation | (i) 0º C – 5º C |
| 2. Benzoic acid | (ii) carrot and Amla |
| 3. Murabba | (iii) X – Ray |
| 4. Pasteurization | (iv) Chemical preservation |
| 5. Refrigeration | (v) 62º C |
Answer :
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Irradiation | (iii) X – Ray |
| 2. Benzoic acid | (iv) Chemical preservation |
| 3. Murabba | (ii) carrot and Amla |
| 4. Pasteurization | (v) 62º C |
| 5. Refrigeration | (i) 0º C – 5º C |
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 90)
Ch-8 Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
1. Give one or two words for the following statements:
(a) Mould that gives penicillin.
(b) Structures produced by a fungus to absorb nutrients from the medium.
(c) Fungi that derive food from dead organic matter.
(d) Hyphae of Rhiz0pus that penetrate into the food material.
(e) Bacteria that cannot live without oxygen.
(f) The common name of Rhizopus and Mucor.
(g) The common name of Saccharomyces.
(h) Name the substance that makes the cell wall of a fungus.
Answer:
(a) Penicillium
(b) Rhizoidal hyphae
(c) Saprophytes
(c) Sporophytes
(d) Mycelium
(e) Anaerobic bacteria
(f) Bread mould, Common pirmould
(g) Bakers yeast
(h) Chitin
2. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) The most common variety of cultivated mushroom is ………………
(b) Pasteurization is used for preserving …………………..
(c) One of the chemicals used for preserving food is ………………
(d) Button mushroom is an ……………… mushroom.
(e) Sterilisation is carried out at temperature above ………………….. .
Answer:
(a) Button Mushroom
(b) Milk
(c) Sodium nenzoate
(d) Agaricus
(e) 110º
3. Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Large fungi | (i) Aspergillus |
| 2. Amylase | (ii) Yeast |
| 3. Fermentation | (iii) Mushroom |
| 4. Rhizobium | (iv) Bioweapon |
| 5. Bacillus anthracis | (v) Nitrogen Fixation |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Large fungi | (iii) Mushroom |
| 2. Amylase | (i) Aspergillus |
| 3. Fermentation | (ii) Yeast |
| 4. Rhizobium | (v) Nitrogen Fixation |
| 5. Bacillus anthracis | (iv) Bioweapon |
Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
B. Short Answer Type Questions (Page 103)
1. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Bacteria are a kind of plants.
(b) Bacteria are both useful and harmful to mankind.
Answer:
(a) Bacteria are a kind of plants because The plant cell possesses a cell wall which is composed of cellulose, pectin and lignin. The cell wall provides mechanical strength and protection to the internal cellular organelles. The bacterial cell also possesses a cell wall which is made up of peptidoglycan. Due to the presence of the cell wall, the bacteria were also considered similar to the plant cell.
(b) Bacteria are both useful and harmful to mankind.
Useful bacteria:
Any bacteria that are beneficial to the human body are defined as good or useful bacteria. They are both naturally present and man-installed. For example, many of the useful bacteria reside in our gut and help us in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. One such bacteria is probiotics.
Other examples of good or useful bacteria are:
–Lactobacillus acidophilus– It converts milk into curd and is usually found residing in the human small intestine.
–Pseudomonas putida, Dechloromonas aromatica, Deinococcus radiodurans – these specific bacteria help in bioremediation.
-Human insulin is produced in the lab from common bacteria. The bacterium Escherichia coli is by far the most widely used.
Harmful bacteria:
A bacteria which causes the infection is called a pathogenic or harmful bacteria. They come from external influences such as food, environmental toxins, or even stress. They are responsible for many infectious diseases like pneumonia, tuberculosis, diphtheria, syphilis, tooth decay. Their effects can be rectified by taking antibiotics and prescribed medication. Some of the examples of harmful bacteria are:
–E.coli can cause serious illness, severe food poisoning, as well as meningitis, and infections can be caused by E.coli.
–Neisseria gonorrhoeae cause gonorrhea. It spreads through sexual contact and causes various infections in both men and women.
-Tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria has been known by many names including scrofula and the White Plague,
-Some strains of one of the better known ‘superbugs’ because of a consistent presence in hospitals around the world, spread a type of diarrhea that can lead to complications in the colon.
2. Explain the following terms:
(a) Botulism
(b) Nitrogen fixation
(c) Nitrification
Answer:
(a) Botulism:– Botulism: An uncommon, but potentially very serious illness, a type of food poisoning, that produces paralysis of muscles via a nerve toxin called botulinum toxin (“botox”) that is manufactured by bacteria named Clostridium botulinum
(b) Nitrogen fixation:–nitrogen fixation, any natural or industrial process that causes free nitrogen (N2), which is a relatively inert gas plentiful in air, to combine chemically with other elements to form more-reactive nitrogen compounds such as ammonia, nitrates, or nitrites
(c) Nitrification :- Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite followed by the oxidation of the nitrite to nitrate occurring through separate organisms or direct ammonia oxidation to nitrate in comammox bacteria. … Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil
3. Give one important function of bacteria in
(a). Medicine
b) Agriculture
(c) Industry
Answer:
(a). Medicine : –Streptomyces-The prescription antibiotics that are used to treat bacterial infections are produced using Streptomyces. They are also used to produce antifungal agents and associated medicines, namely – immunosuppressants which are remedial measures prescribed by doctors for certain autoimmune diseases
b) Agriculture :- -A bacteria Rhizobium found in the soil supplies ammonia to the plants, which is essential for the growth of the plants.
(c) Industry :—Lactobacillus acidophilus– It converts milk into curd and is usually found residing in the human small intestine.
C. Long Answer Type Questions (Page 91)
Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
1. Name commonly grown mushrooms. How are mushrooms cultivated? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Major steps in the cultivation of common edible mushrooms:
(1) Composting: Composting involves mixing various components such as wheat or paddy straw, chicken manure and organic and inorganic fertilizers in a fixed proportion. The temperature of the compost is maintained at around 50C. The compost is kept undisturbed for about one week.
(2) Spawning: ‘Mushroom seed’ in the form of mycelium of mushroom to be grown is introduced into the heap of compost and left for spreading for around two days.
(3) Casing: Casing is the most important step in mushroom cultivation. It involves the spreading of a thin layer of soil over the compost. This provides humidity and support to the mushroom. It also serves to prevent the desiccation of the compost heap and helps in temperature regulation at around 20C-25C to forbid the growth of pests and diseases. The provision for circulating air around the compost bed should also be made.
(4) Cropping and harvesting: Three major growth stages are observed before mushrooms attain a fully grown form. Firstly, the mycelium, i.e. a network of fibrous mass, spreads out in 2 to 6 weeks, followed by the tiny pin head stage and finally the button stage, which is marked by an increase in the mushroom size, until it acquires marketable size.
(5) Preservation: Mushrooms have a very short shelf-life. Processes such as vacuum cooling, bombardment by gamma radiation, followed by storage at 15C, freeze drying in a solution of citric acid, ascorbic acid and brine, etc. are used for the preservation of mushrooms.
2. What are the uses of yeast?
Answer:
- Bread. The most common use of yeast has been in the making of bread. …
- Alcoholic Drinks. Brewing wine and beer has also used yeast for centuries to ferment the mixture to make it alcoholic. …
- Non-Alcoholic Drinks. …
- Scientific Research. …
- Biofuel. …
- Probiotics. …
- Yeast Extract.
3. What are bioweapons? How do they create bioterrorism?
Answer:
Biological weapons are microorganisms like virus, bacteria, fungi, or other toxins that are produced and released deliberately to cause disease and death in humans, animals or plants. … Bioterrorism attacks could also result in an epidemic, for example if Ebola or Lassa viruses were used as the biological agent
4. Write any three useful effects of bacteria for the environment.
Answer:
Certain bacteria can break down toxic pollutants. … Bacteria help degrade dead animals and plants and bring valuable nutrients back to Earth. Some species also help clean harmful pollutants out of the environment in a process called bioremediation
5. What are antibiotics? Give two examples of antibiotics. Which organisms, bacteria or fungi are used for the production of antibiotics?
Answer:
6. What is pasteurisation? Where is it employed?
Answer:
pasteurization is used widely in the dairy industry and other food processing industries to achieve food preservation and food safety. … Due to the mild heat, there are minor changes to the nutritional quality and sensory characteristics of the treated foods
7. What is the role of bacteria in agriculture?
Answer:
Bacteria provide large quantities of nitrogen to plants and nitrogen is often lacking in the soil. Many bacteria secrete enzymes in the soil to makes phosphorus more soluble and plant available
8. Give one similarity between fungi and animals
Answer:
animal and fungi both have heterotrophic mode of nutrition and both of them are multicellular
9. What are moulds? Name them. Where do they grow?
Answer:
Molds are very common in buildings and homes and will grow anywhere indoors where there is moisture. The most common indoor molds are Cladosporium, Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Alternaria
10. Give special features of bacteria which contribute to universal distribution of bacteria.
Answer: -Extremely simple structure. Small size and large surface to volume ratio. Resistance of vegetative cells to adverse environmental factors. Formation of highly resistant spores
D. Multiple Choice Questions (Page 103)
Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Choose the correct answer.
1. The fungi that are used as food are:
(a) Slime moulds
(b) Mushrooms
(c) Mildews
(d) Yeast
Answer: (b) Mushrooms
2. Rhizopus is commonly known as
(a) Crown gall
(b) Black mould
(c) Green mould
(d) Blue mould
Answer: (b) Black mould
3. Production of ethanol (C2H5OH) occurs in one of the life processes of the life
(a) Bread mould
(b) Yeast
(c) Mushroom
(d) Penicillium
Answer: (b) Yeast
E Application/Skill-based Question (Page 103)
Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
1. (a) Which process is shown in the given picture?
(b) Which bacteria is responsible of this process?
(c) Name the plants to which this process is applied.

Answer:
(a) Retting of Fibres
(b) Clostridium butylicum
(c) Jute, Hemp and Flex fibers
2. The given picture shows the roots of a legume plant.
Answer the following questions:
(a) What is found in these nodules?
(b) What is the role of nodules in the nature?
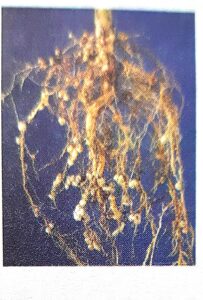
Answer:
(a) Rhizobium bacteria
(b) These bacteria convert and fix up free increase its fertility.
Thanks




Thank yo so much! 🙏🙏🙏. This website is so helpful for students for the answer . Great job
thanks for positive response
Thank you