Triangles Concise Class-9th ICSE Mathematics Selina Publications Solutions Chapter-9 (Congruency in Triangles). We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-9 Triangles for ICSE Class-9 Concise Selina Mathematics by R K Bansal.
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-9 A and Exe-9 B, to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics .
Triangles Concise Class-9th ICSE Mathematics Selina Publications Solutions Chapter-9 (Congruency in Triangles).
–: Select Topics :–
Exercise – 9 A, Triangles Concise Class-9th ICSE Mathematics Selina Publications Solutions (Congruency in Triangles)
Question 1
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? In each case, state the condition of congruency:
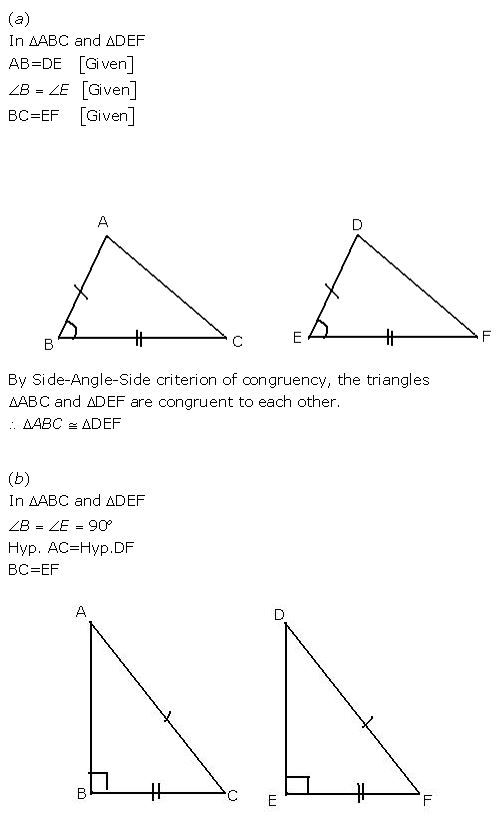
(a) In ΔABC and ΔDEF, AB = DE, BC = EF and B = E.
(b) In ΔABC and ΔDEF, B = E = 90o; AC = DF and BC = EF.
(c) In ΔABC and Δ QRP, AB = QR, B = R and C = P.
(d) In ΔABC and Δ PQR, AB = PQ, AC = PR and BC = QR.
(e) In ΔADC and Δ PQRΔ, BC = QR, A = 90o, C = R = 40o and Q = 50o.
( f) In Triangle ABC and Triangle BCD ………………………..
Answer
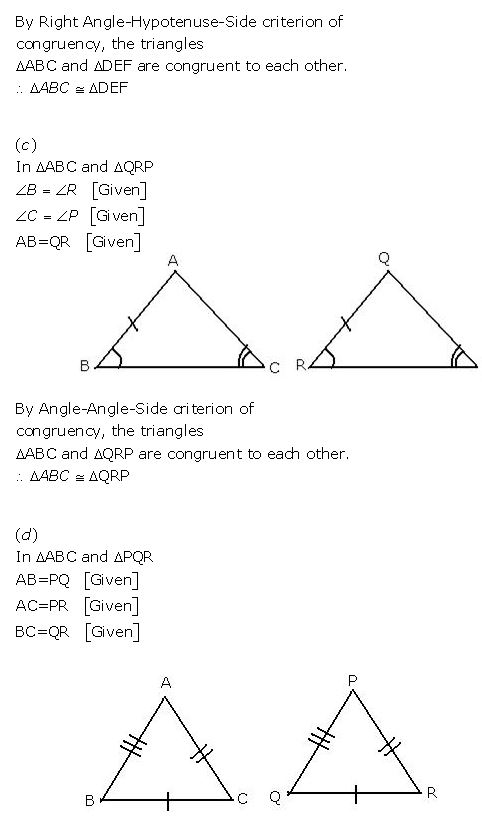
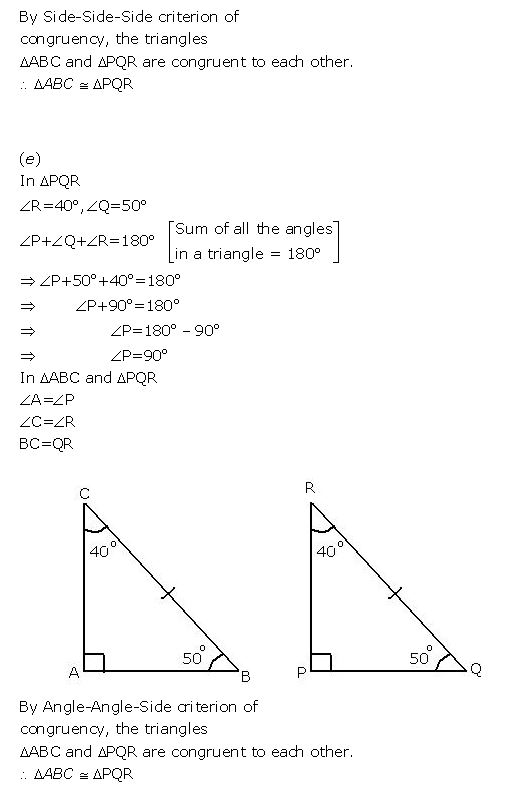
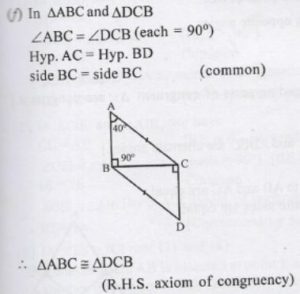
Question 2
The given figure shows a circle with centre O. P is mid-point of chord AB.
…………….
Show that OP is perpendicular to AB
Answer
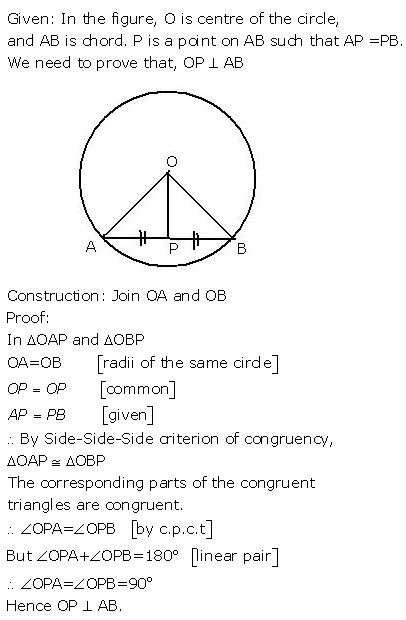
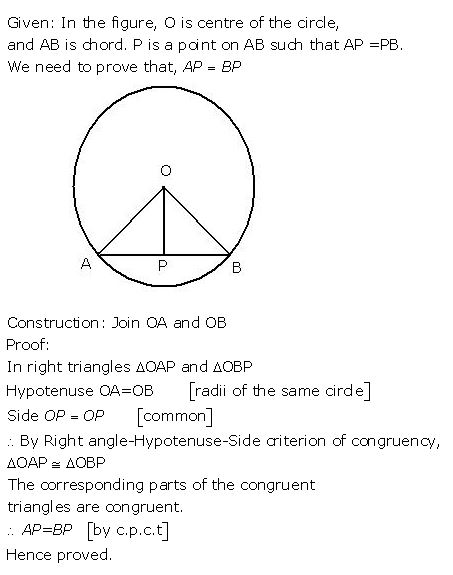
Question 3
The following figure shows a circle with centre O.
If OP is perpendicular to AB, prove that AP = BP.
Answer
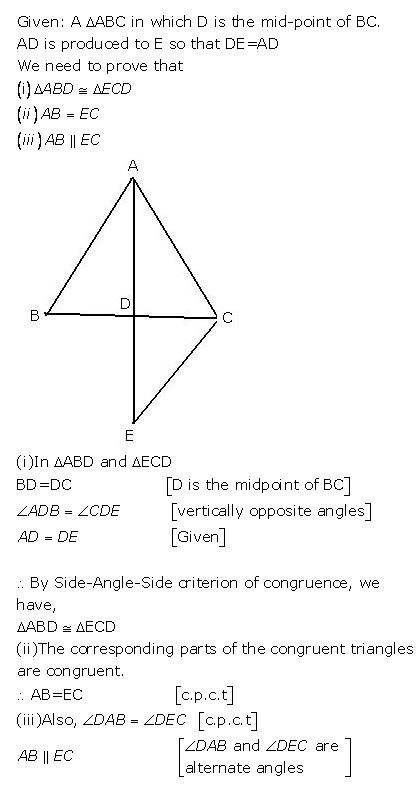
Question 4
In a triangle ABC, D is mid-point of BC; AD is produced upto E so that DE = AD. Prove that:
(i) ABD and ECD are congruent.
(ii) AB = CE.
(iii) AB is parallel to EC.
Answer
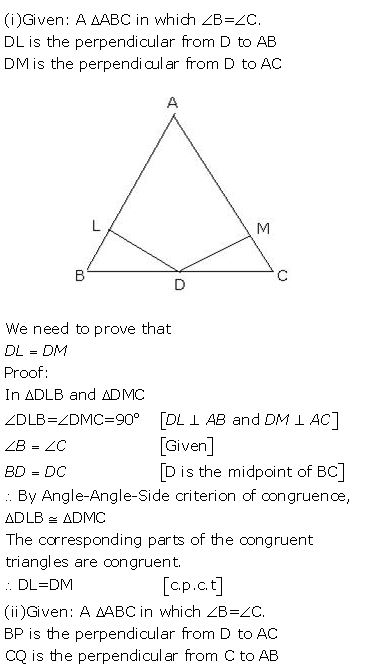
Question 5
A triangle ABC has B = C.
Prove that:
(i) The perpendiculars from the mid-point of BC to AB and AC are equal.
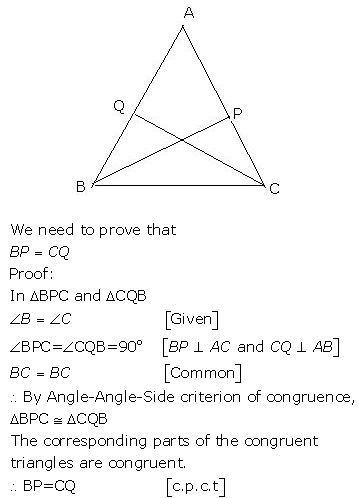
(ii) The perpendiculars form B and C to the opposite sides are equal.
Answer
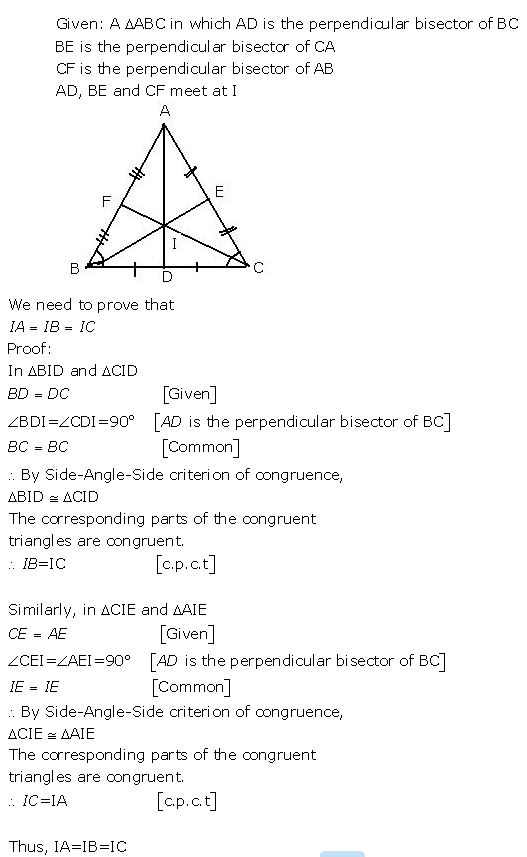
Question 6
The perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle ABC meet at I.
Prove that: IA = IB = IC.
Answer
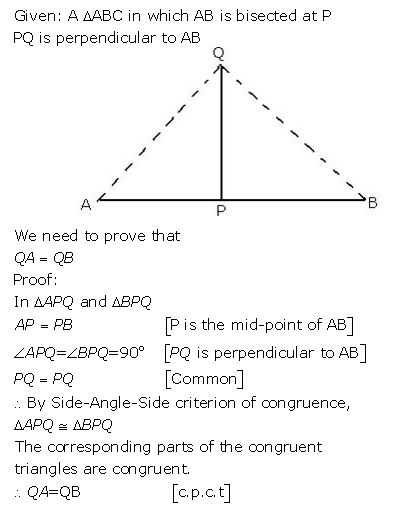
Question 7
A line segment AB is bisected at point P and through point P another line segment PQ, which is perpendicular to AB, is drawn. Show that: QA = QB.
Answer
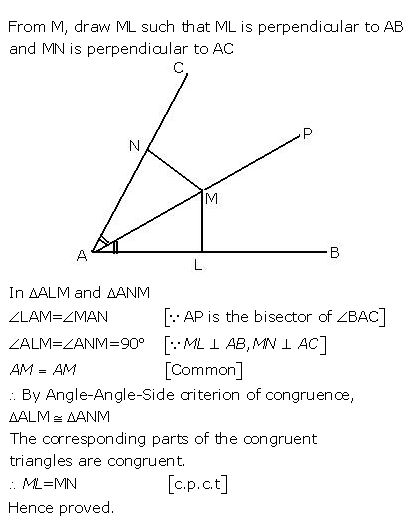
Question 8
If AP bisects angle BAC and M is any point on AP, prove that the perpendiculars drawn from M to AB and AC are equal.
Answer
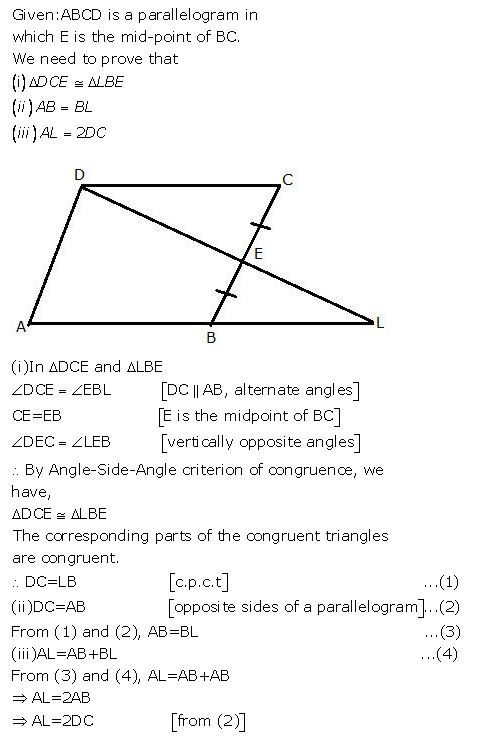
Question 9
From the given diagram, in which ABCD is a parallelogram, ABL is al line segment and E is mid point of BC.
Prove that:
(i) DCE LBE
(ii) AB = BL.
(iii) AL = 2DC
Answer
Question 10
In the given figure, AB = DB and Ac = DC.
If ABD = 58o,
DBC = (2x – 4)o,
ACB = y + 15o and
DCB = 63o ; find the values of x and y.
Answer

Question 11
In the given figure: AB//FD, AC//GE and BD = CE; prove that:
(i) BG = DF
(ii) CF = EG
Answer

Question 12
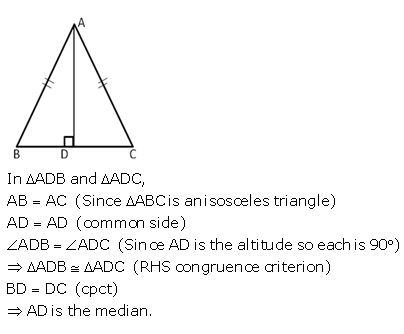
In ∆ABC, AB = AC. Show that the altitude AD is median also.
Answer
Question 13
In the following figure, BL = CM.
Prove that AD is a median of triangle ABC.
Answer
Question 14
In the following figure, AB = AC and AD is perpendicular to BC. BE bisects angle B and EF is perpendicular to AB.
Prove that :
(i) BD = CD
(ii) ED = EF
Answer

Question 15
Use the information in the given figure to prove :
(i) AB = FE
(ii) BD = CF
Answer

Selina Publications Solutions Triangles Concise Class-9th ICSE Mathematics (Congruency in Triangles) Exercise – 9 B
Question 1
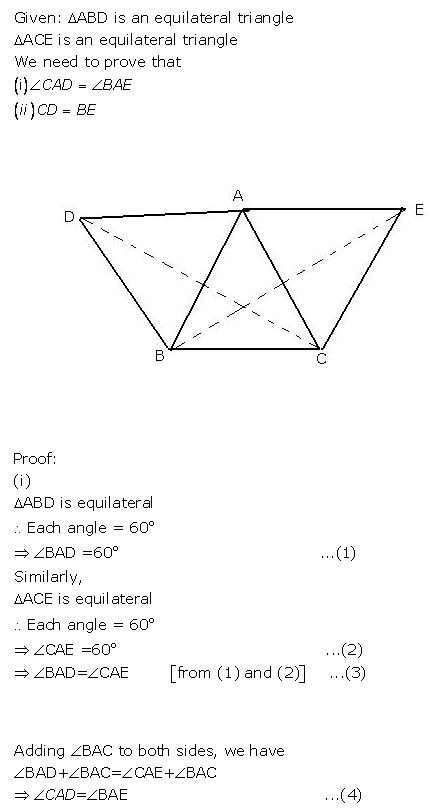
On the sides AB and AC of triangle ABC, equilateral triangle ABD and ACE are drawn.
Prove that: (i) CAD = BAE (ii) CD = BE.
Answer

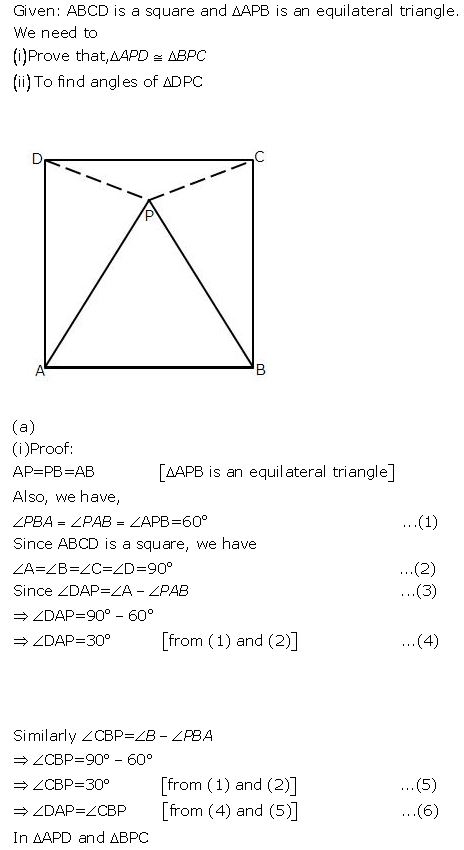
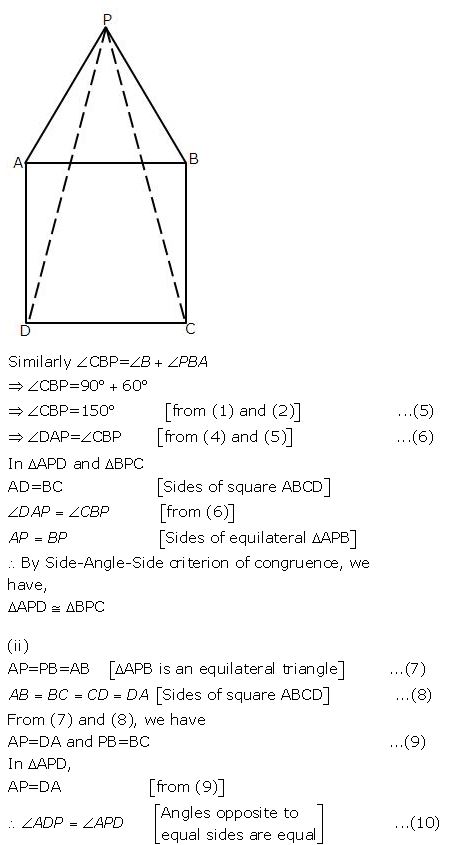
Question 2
In the following diagrams, ABCD is a square and APB is an equilateral triangle.
In each case,
(i) Prove that: .ΔAPD = Δ BPC
(ii) Find the angles of .Δ DPC
Answer



Question 3
In the figure, given below, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. ABPQ and ACRS are squares. Prove that:
(i) .Δ ACQ and .Δ ASB are congruent.
(ii) CQ = BS
Answer

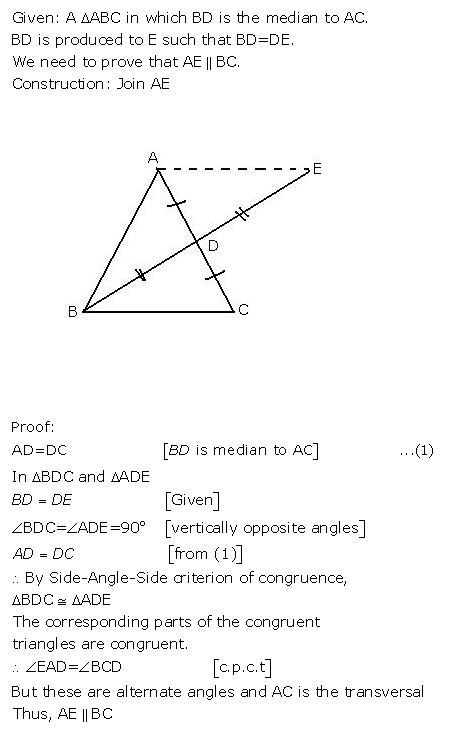
Question 4
In a ΔABC, BD is the median to the side AC, BD is produced to E such that BD = DE. Prove that: AE is parallel to BC.
Answer
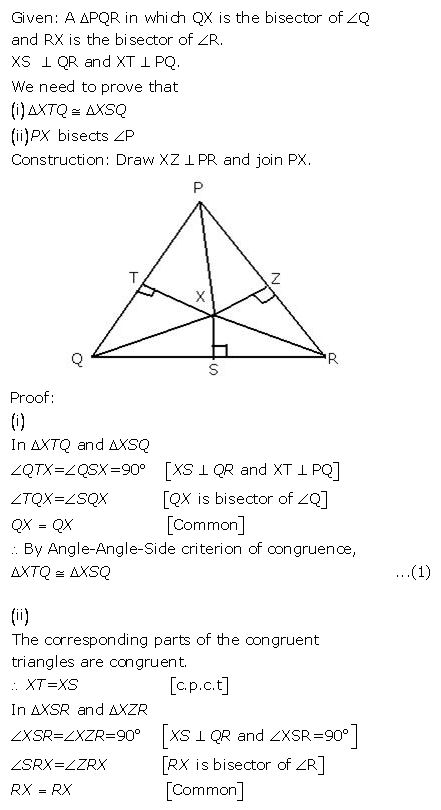
Question 5
In the adjoining figure, OX and RX are the bisectors of the angles Q and R respectively of the triangle PQR.
If XS QR and XT PQ ; prove that:
(i) ……………………..
(ii) PX bisects angle P.
Answer

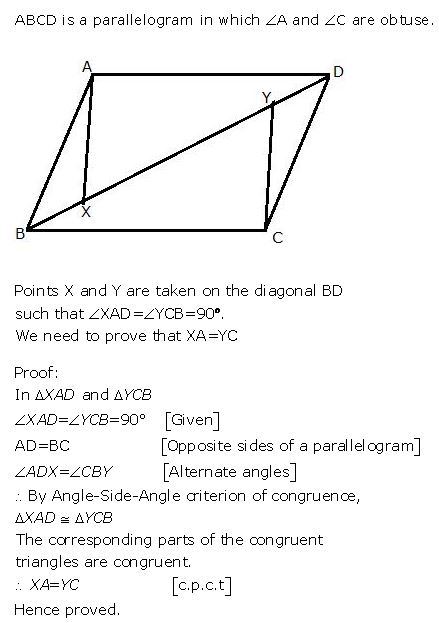
Question 6
In the parallelogram ABCD, the angles A and C are obtuse. Points X and Y are taken on the diagonal BD such that the angles XAD and YCB are right angles.
Prove that: XA = YC.
Answer
Question 7
ABCD is a parallelogram. The sides AB and AD are produced to E and F respectively, such produced to E and F respectively, such that AB = BE and AD = DF.
Prove that: Δ BEC=Δ DCF.
Answer
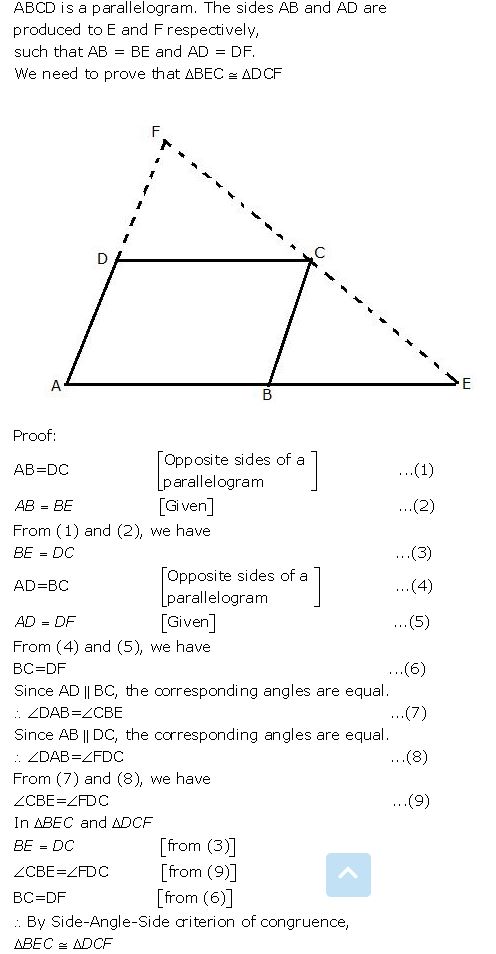
Hence proved
Question 8
In the following figures, the sides AB and BC and the median AD of triangle ABC are equal to the sides PQ and QR and median PS of the triangle PQR. Prove that ABC and PQR are congruent.
Answer

Question 9
In the following diagram, AP and BQ are equal and parallel to each other.
Prove that:
(i) ……………………
(ii) AB and PQ bisect each other.
Answer

Question 10
In the following figure, OA = OC and AB = BC.
Prove that:
(i) AOB = 90o
(ii) triangle AOD =triangle COD
(iii) AD = CD
Answer
Question 11
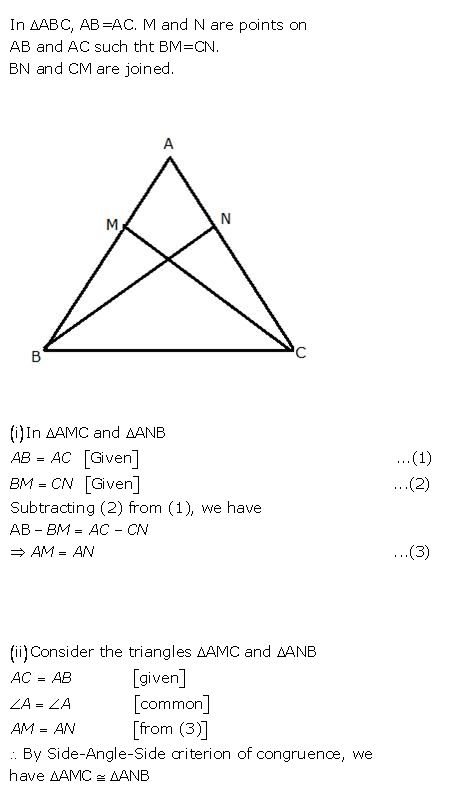
The following figure shown a triangle ABC in which AB = AC. M is a point on AB and N is a point on AC such that BM = CN.
Prove that:
(i) AM = AN (ii)triangle AMC = triangle ANB
(iii) BN = CM (iv) triangle BMC = triangle CNB
Answer
Question 12
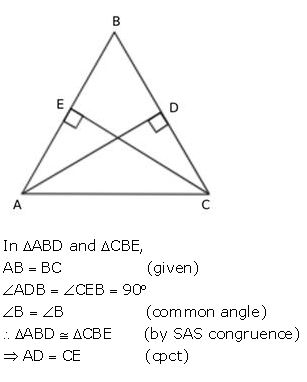
In a triangle ABC, AB = BC, AD is perpendicular to side BC and CE is perpendicular to side AB. Prove that : AD = CE.
Answer
Question 13
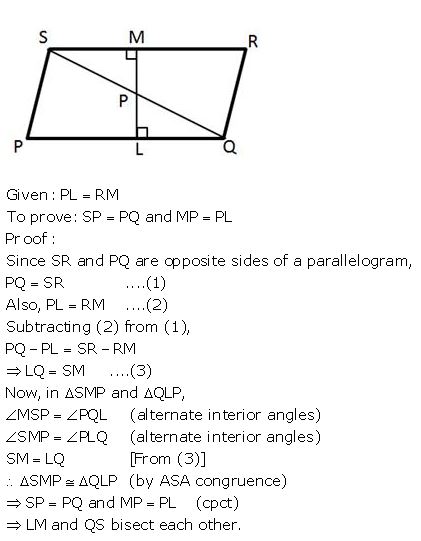
PQRS is a parallelogram. L and M are points on PQ and SR respectively such that PL= MR. Show that LM and QS bisect each other.
Answer
Question 14
In the following figure, ABC is an equilateral triangle in which QP is parallel to AC. Side AC is produced upto point R so that CR = BP.
Prove that QR bisects PC.
Hint: (Show that ∆ QBP is equilateral
⇒ BP = PQ, but BP = CR
⇒ PQ = CR ⇒ ∆ QPM ≅ ∆ RCM)
Answer

Question 15
In the following figure, ∠A = ∠C and AB = BC. Prove that ΔABD ≅ ΔCBE.
Answer

Question 16
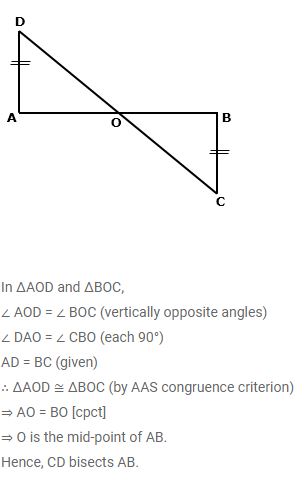
AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to a line segment AB. If AD and BC are on different sides of AB prove that CD bisects AB.
Answer
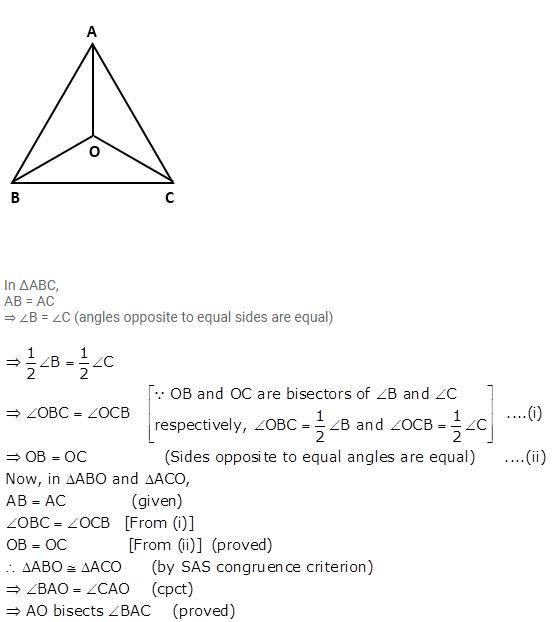
Question 17
In ΔABC, AB = AC and the bisectors of angles B and C intersect at point O. Prove that :
(i) BO = CO
(ii) AO bisects angle BAC.
Answer
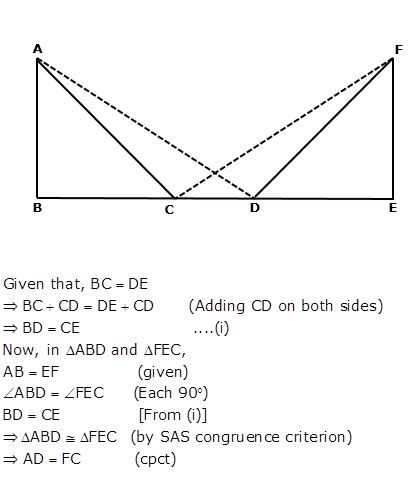
Question 18
In the following figure, AB = EF, BC = DE and ∠B = ∠E = 90°.
Prove that AD = FC.
Answer
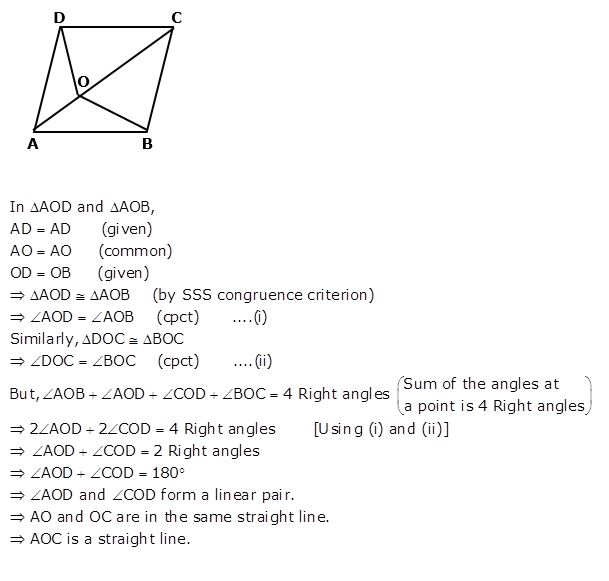
Question 19
A point O is taken inside a rhombus ABCD such that its distance from the vertices B and D are equal. Show that AOC is a straight line.
Answer
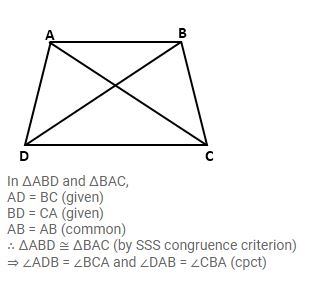
Question 20
In quadrilateral ABCD, AD = BC and BD = CA. Prove that:
(i) ∠ADB = ∠BCA
(ii) ∠DAB = ∠CBA
Answer
— End of Triangles Concise Class-9th ICSE Solutions :–
Return to – Concise Selina Maths Solutions for ICSE Class -9
Thanks